CAR T-cell product performance in haematological malignancies before and after marketing authorisation
- PMID: 32007196
- PMCID: PMC7841982
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30729-6
CAR T-cell product performance in haematological malignancies before and after marketing authorisation
Abstract
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells represent a potent new approach to treat haematological malignancies. Two CAR T-cell therapies, tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel, have been approved in Europe and the USA, as well as several other countries, for the treatment of leukaemia and lymphoma. These approvals marked a major milestone in the field of cell and gene therapies. However, the clinical development and regulatory evaluation of these innovative therapies faced several challenges that are considered important lessons learned for future similar products. Here, we examine the products' non-clinical and clinical data packages to outline the challenges encountered during the regulatory evaluation process in Europe, and to provide an update on their performance after authorisation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
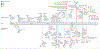
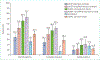

References
-
- Vormittag P, Gunn R, Ghorashian S, Veraitch FS. A guide to manufacturing CAR T cell therapies. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2018; 53: 164–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

