K562 erythroleukemia line as a possible reticulocyte source to culture Plasmodium vivax and its surrogates
- PMID: 32007479
- PMCID: PMC7097847
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2020.01.012
K562 erythroleukemia line as a possible reticulocyte source to culture Plasmodium vivax and its surrogates
Abstract
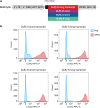
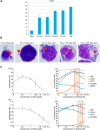
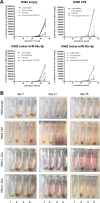
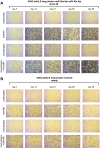
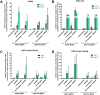
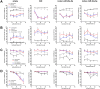
Establishing an in vitro "red blood cell matrix" that would allow uninterrupted access to a stable, homogeneous reticulocyte population would facilitate the establishment of continuous, long-term in vitro Plasmodium vivax blood stage cultures. In this study, we have explored the suitability of the erythroleukemia K562 cell line as a continuous source of such reticulocytes and have investigated regulatory factors behind the terminal differentiation (and enucleation, in particular) of this cell line that can be used to drive the reticulocyte production process. The Duffy blood group antigen receptor (Fy), essential for P. vivax invasion, was stably introduced into K562 cells by lentiviral gene transfer. miRNA-26a-5p and miRNA-30a-5p were downregulated to promote erythroid differentiation and enucleation, resulting in a tenfold increase in the production of reticulocytes after stimulation with an induction cocktail compared with controls. Our results suggest an interplay in the mechanisms of action of miRNA-26a-5p and miRNA-30a-5p, which makes it necessary to downregulate both miRNAs to achieve a stable enucleation rate and Fy receptor expression. In the context of establishing P. vivax-permissive, stable, and reproducible reticulocytes, a higher enucleation rate may be desirable, which may be achieved by the targeting of further regulatory mechanisms in Fy-K562 cells; promoting the shift in hemoglobin production from fetal to adult may also be necessary. Despite the fact that K562 erythroleukemia cell lines are of neoplastic origin, this cell line offers a versatile model system to research the regulatory mechanisms underlying erythropoiesis.
Copyright © 2020 ISEH -- Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Erythrocyte Binding Protein of Plasmodium vivax Suggests an Alternate Invasion Pathway into Duffy-Positive Reticulocytes.mBio. 2016 Aug 23;7(4):e01261-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01261-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27555313 Free PMC article.
-
Duffy antigen expression on reticulocytes does not alter following blood loss in an autologous donation model.Vox Sang. 2009 Oct;97(3):268-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.2009.01203.x. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Vox Sang. 2009. PMID: 19552696
-
Southeast Asian ovalocytosis is associated with increased expression of Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC).Immunohematology. 2009;25(2):63-6. Immunohematology. 2009. PMID: 19927622
-
The biology of unconventional invasion of Duffy-negative reticulocytes by Plasmodium vivax and its implication in malaria epidemiology and public health.Malar J. 2020 Aug 24;19(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-03372-9. Malar J. 2020. PMID: 32831093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and cellular interactions defining the tropism of Plasmodium vivax for reticulocytes.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2018 Dec;46:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30366310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel evidence that the ABO blood group shapes erythropoiesis and results in higher hematocrit for blood group B carriers.Leukemia. 2023 May;37(5):1126-1137. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01858-4. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Leukemia. 2023. PMID: 36854778 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MiRNA in the Regulation of Blood Group Expression.Transfus Med Hemother. 2024 Jun 4;51(4):237-251. doi: 10.1159/000538866. eCollection 2024 Aug. Transfus Med Hemother. 2024. PMID: 39135851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The challenges of Plasmodium vivax human malaria infection models for vaccine development.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1006954. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006954. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeo JH, McAllan BM, Fraser ST. Scanning electron microscopy reveals two distinct classes of erythroblastic island isolated from adult mammalian bone marrow. Microsc Microanal. 2016;22:368–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

