Epithelial cell function and remodeling in nasal polyposis
- PMID: 32007569
- PMCID: PMC11784937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.01.018
Epithelial cell function and remodeling in nasal polyposis
Abstract
Objective: To review the latest discoveries on airway epithelial cell diversity and remodeling in type 2 inflammation, including nasal polyposis.
Data sources: Reviews and primary research manuscripts were identified from PubMed, Google, and Bioarchives, using the search words airway epithelium, nasal polyposis, or chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis AND basal cell, ciliated cell, secretory cell, goblet cell, neuroendocrine cell, pulmonary neuroendocrine cell, ionocyte, brush cell, solitary chemosensory cell, microvillus cell, or tuft cell.
Study selections: Studies were selected based on novelty and likely relevance to airway epithelial innate immune functions or the pathobiology of type 2 inflammation.
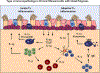
Results: Airway epithelial cells are more diverse than previously appreciated, with specialized subsets, including ionocytes, solitary chemosensory cells, and neuroendocrine cells that contribute to important innate immune functions. In chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, the composition of the epithelium is significantly altered. Loss of ciliated cells and submucosal glands and an increase in basal airway epithelial progenitors leads to loss of innate immune functions and an expansion of proinflammatory potential. Type 2 cytokines play a major role in driving this process.
Conclusion: Airway epithelial remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis is extensive, leading to loss of innate immune function and enhanced proinflammatory potential. The mechanisms driving airway remodeling and its sequelae deserve further attention before restitution of epithelial differentiation can be considered a reasonable therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ordovas-Montanes J, Dwyer DF, Nyquist SK, Buchheit KM, Vukovic M, Deb C, Wadsworth MH 2nd, Hughes TK, Kazer SW, Yoshimoto E, Cahill KN, Bhattacharyya N, Katz HR, Berger B, Laidlaw TM, Boyce JA, Barrett NA, Shalek AK. 2018. Allergic inflammatory memory in human respiratory epithelial progenitor cells. Nature 560: 649–54 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vieira Braga FA, Kar G, Berg M, Carpaij OA, Polanski K, Simon LM, Brouwer S, Gomes T, Hesse L, Jiang J, Fasouli ES, Efremova M, Vento-Tormo R, Talavera-Lopez C, Jonker MR, Affleck K, Palit S, Strzelecka PM, Firth HV, Mahbubani KT, Cvejic A, Meyer KB, Saeb-Parsy K, Luinge M, Brandsma CA, Timens W, Angelidis I, Strunz M, Koppelman GH, van Oosterhout AJ, Schiller HB, Theis FJ, van den Berge M, Nawijn MC, Teichmann SA. 2019. A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma. Nat Med 25: 1153–63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

