Intractable Hepatic Encephalopathy with a Large Portosystemic Shunt Successfully Treated Using Shunt-preserving Disconnection of the Portal and Systemic Circulation
- PMID: 32009096
- PMCID: PMC7205523
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3955-19
Intractable Hepatic Encephalopathy with a Large Portosystemic Shunt Successfully Treated Using Shunt-preserving Disconnection of the Portal and Systemic Circulation
Abstract
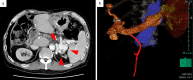
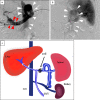
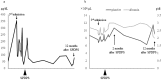
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a significant symptom of decompensated liver cirrhosis. Occlusion of portosystemic shunts is used to treat refractory HE. Nevertheless, these treatments often cause adverse events, such as ascites and esophageal varices. We treated a 57-year-old man with refractory HE using shunt-preserving disconnection of the portal and systemic circulation (SPDPS). After SPDPS, there were no obvious complications, and the patient's ammonia level significantly decreased. To date, the patient has not experienced recurrent HE. SPDPS appears to be a safe and effective treatment method for portosystemic encephalopathy.
Keywords: hepatic encephalopathy; percutaneous transsplenic access; shunt-preserving disconnection of the portal and systemic circulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Reversal of portal-systemic encephalopathy by shunt-preserving disconnection of portal and systemic circulation].Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Feb;93(2):96-103. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8865749 Japanese.
-
Embolization of splenorenal shunt associated to portal vein thrombosis and hepatic encephalopathy.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Nov 14;20(42):15910-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15910. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25400477 Free PMC article.
-
Shunt-preserving disconnection of the portal to systemic circulation in patients with hepatic encephalopathy.Acta Radiol. 2018 Apr;59(4):441-447. doi: 10.1177/0284185117722810. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Acta Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28791885
-
Hepatic encephalopathy in non-cirrhotic portal hypertension.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 16;40(1):103. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01522-5. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39821852 Review.
-
[Portosystemic shunts versus endoscopic therapy for esophageal varices after the first bleeding: does the Cochrane analysis give a complete answer?].Ugeskr Laeger. 2007 Aug 20;169(34):2761-3. Ugeskr Laeger. 2007. PMID: 17878011 Review. Danish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hepatic encephalopathy due to extrahepatic portosystemic shunt.Clin Case Rep. 2020 Jun 1;8(9):1852-1853. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2986. eCollection 2020 Sep. Clin Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32983517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weissenborn K. Portosystemic encephalopathy. Handb Clin Neurol 120: 661-674, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Hanna SS, Smith RS Jr, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Warren WD. Reversal of hepatic encephalopathy after occlusion of total portasystemic shunts. Am J Surg 142: 285-29, 1982. - PubMed
-
- Potts JR 3rd, Henderson JM, Millikan WJ Jr, Sones P, Warren WD. Restoration of portal venous perfusion and reversal of encephalopathy by balloon occlusion of portal systemic shunt. Gastroenterology 87: 208-212, 1984. - PubMed
-
- Uflacker R, Silva Ade O, d'Albuquerque LA, Piske RL, Mourao GS. Chronic portosystemic encephalopathy: embolization of portosystemic shunts. Radiology 165: 721-725, 1987. - PubMed
-
- Kawanaka H, Ohta M, Hashizume M, et al. . Portosystemic encephalopathy treated with balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration. Am J Gastroenterol 90: 508-510, 1995. - PubMed

