Reactive Jumps Preserve Skeletal Muscle Structure, Phenotype, and Myofiber Oxidative Capacity in Bed Rest
- PMID: 32009969
- PMCID: PMC6974579
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01527
Reactive Jumps Preserve Skeletal Muscle Structure, Phenotype, and Myofiber Oxidative Capacity in Bed Rest
Abstract
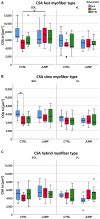
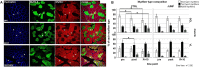
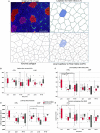
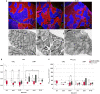
Identification of countermeasures able to prevent disuse-induced muscle wasting is crucial to increase performance of crew members during space flight as well as ameliorate patient's clinical outcome after long immobilization periods. We report on the outcome of short but high-impact reactive jumps (JUMP) as countermeasure during 60 days of 6° head-down tilt (HDT) bed rest on myofiber size, type composition, capillarization, and oxidative capacity in tissue biopsies (pre/post/recovery) from the knee extensor vastus lateralis (VL) and deep calf soleus (SOL) muscle of 22 healthy male participants (Reactive jumps in a sledge, RSL-study 2015-2016, DLR:envihab, Cologne). Bed rest induced a slow-to-fast myofiber shift (type I ->II) with an increased prevalence of hybrid fibers in SOL after bed rest without jumps (control, CTRL, p = 0.016). In SOL, JUMP countermeasure in bed rest prevented both fast and slow myofiber cross-sectional area (CSA) decrements (p = 0.005) in CTRL group. In VL, bed rest only induced capillary rarefaction, as reflected by the decrease in local capillary-to-fiber ratio (LCFR) for both type II (pre vs. post/R + 10, p = 0.028/0.028) and type I myofibers (pre vs. R + 10, p = 0.012), which was not seen in the JUMP group. VO2 max Fiber (pL × mm-1 × min-1) calculated from succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-stained cryosections (OD660 nm) showed no significant differences between groups. High-impact jump training in bed rest did not prevent disuse-induced myofiber atrophy in VL, mitigated phenotype transition (type I - >II) in SOL, and attenuated capillary rarefaction in the prime knee extensor VL however with little impact on oxidative capacity changes.
Keywords: bed rest; capillarization; countermeasure; disuse; muscle atrophy; oxidative capacity.
Copyright © 2020 Blottner, Hastermann, Weber, Lenz, Gambara, Limper, Rittweger, Bosutti, Degens and Salanova.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

