Effects of Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) and D3 (Cholecalciferol) on Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Primary Macrophage Immune Response to Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida Infection
- PMID: 32010129
- PMCID: PMC6973134
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03011
Effects of Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol) and D3 (Cholecalciferol) on Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Primary Macrophage Immune Response to Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida Infection
Abstract
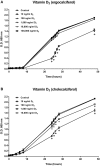
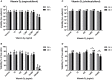
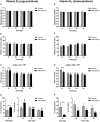
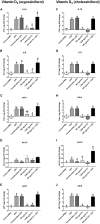
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) are fat-soluble secosteroid hormones obtained from plant and animal sources, respectively. Fish incorporates vitamin D2 and D3 through the diet. In mammals, vitamin D forms are involved in mineral metabolism, cell growth, tissue differentiation, and antibacterial immune response. Vitamin D is an essential nutrient in aquafeeds for finfish. However, the influence of vitamin D on fish cell immunity has not yet been explored. Here, we examined the effects of vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 on Salmo salar primary macrophage immune response to A. salmonicida subspecies salmonicida infection under in vitro conditions. We determined that high concentrations of vitamin D2 (100,000 ng/ml) and D3 (10,000 ng/ml) affect the growth of A. salmonicida and decrease the viability of S. salar primary macrophages. In addition, we determined that primary macrophages pre-treated with a biologically relevant concentration of vitamin D3 for 24 h showed a decrease of A. salmonicida infection. In contrast, vitamin D2 did not influence the antibacterial activity of the S. salar macrophages infected with A. salmonicida. Vitamin D2 and D3 did not influence the expression of canonical genes related to innate immune response. On the other hand, we found that A. salmonicida up-regulated the expression of several canonical genes and suppressed the expression of leukocyte-derived chemotaxin 2 (lect-2) gene, involved in neutrophil recruitment. Primary macrophages pre-treated for 24 h with vitamin D3 counteracted this immune suppression and up-regulated the transcription of lect-2. Our results suggest that vitamin D3 affects A. salmonicida attachment to the S. salar primary macrophages, and as a consequence, the A. salmonicida invasion decreased. Moreover, our study shows that the positive effects of vitamin D3 on fish cell immunity seem to be related to the lect-2 innate immunity mechanisms. We did not identify positive effects of vitamin D2 on fish cell immunity. In conclusion, we determined that the inactive form of vitamin D3, cholecalciferol, induced anti-bacterial innate immunity pathways in Atlantic salmon primary macrophages, suggesting that its utilization as a component of a healthy aquafeed diet in Atlantic salmon could enhance the immune response against A. salmonicida.
Keywords: Aeromonas salmonicida; Atlantic salmon; Gram-negative; innate immunity; primary macrophages; vitamin D2; vitamin D3.
Copyright © 2020 Soto-Dávila, Valderrama, Inkpen, Hall, Rise and Santander.
Figures
References
-
- Lock EJ, Waagbø R, Wendelaar-Bonga S, Flick G. The significance of vitamin D for fish: a review. Aquac Nutr. (2010) 16:100–16. 10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00722.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

