IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications
- PMID: 32010143
- PMCID: PMC6974482
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03096
IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications
Abstract
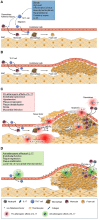
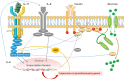
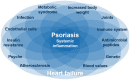
Interleukin 17A (IL-17A) is one of the currently known six members of the IL-17 cytokine family and is implicated in immune responses to infectious pathogens and in the pathogenesis of inflammatory autoimmune diseases like psoriasis. Psoriatic skin is characterized by high expression of IL-17A and IL-17F, which act on immune and non-immune cell types and strongly contribute to tissue inflammation. In psoriatic lesions, IL-17A, IL-17E, and IL-17F are involved in neutrophil accumulation, followed by the formation of epidermal micro abscesses. IL-17A together with other Th17 cytokines also upregulates the production of several chemokines that are implicated in psoriasis pathogenesis. IL17A-targeting antibodies show an impressive clinical efficacy in patients with psoriasis. Studies have reported an improvement of at least 75% as measured by the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) in >80% of patients treated with anti-IL-17A therapy. Psoriasis skin manifestations, cardiovascular as well as metabolic disease in psoriasis appear to share pathogenic mechanisms evolving around IL-17A and its proinflammatory role. Thus, anti-IL-17A therapy not only improves skin manifestations of psoriasis, but also cardiovascular inflammation as well as metabolic factors and different domains of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) including peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and axial involvement. This review summarizes the biological role of IL-17A, before reviewing currently available data on its role in the physiology and pathophysiology of the skin, as well as the cardiovascular and the metabolic system. In conclusion, clinical recommendations for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis based on the current available data are given.
Keywords: IL-17A; cardiovascular; comorbidities; diabetes; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2020 von Stebut, Boehncke, Ghoreschi, Gori, Kaya, Thaci and Schäffler.
Figures
References
-
- Kristensen SL, Ahlehoff O, Lindhardsen J, Erichsen R, Lamberts M, Khalid U, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with an increased risk of hospitalization for heart failure: a Danish Nationwide Cohort study. Circ Heart Fail. (2014) 7:717–22. 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001152 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

