Assessment of the value of 3D-DSA combined with neurointerventional thrombolysis in the treatment of senile cerebrovascular occlusion
- PMID: 32010249
- PMCID: PMC6966151
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8274
Assessment of the value of 3D-DSA combined with neurointerventional thrombolysis in the treatment of senile cerebrovascular occlusion
Abstract
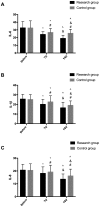
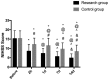
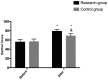
Assessment of the value of three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography (3D-DSA) combined with neurointerventional thrombolysis in the treatment of senile cerebrovascular occlusion was investigated. A total of 129 patients with senile cerebrovascular occlusion admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University from August 2015 to September 2017 were collected. Among them, 69 patients who underwent neurointerventional catheter thrombolysis under 3D-DSA were included in the study group, and 60 patients treated with neurointerventional thrombolysis were the control group. The levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β and IL-8 in the two groups were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) before treatment (T0), 7 days (7d) after treatment (T1) and 14 days (14d) after treatment (T2). The score of the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale and the clinical efficacy of patients in the two groups were compared before and after treatment, and Barthel index (BI) was used for investigation before and after treatment. The recurrence rate of disease in the two groups within 1 year was recorded. At T1, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-8 in the study group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The NIHSS score in the study group was lower than that in the control group after treatment (P<0.05). The BI score in the study group was significantly higher than that in the control group after treatment (P<0.05). After the prognostic follow-up, the disease recurrence rate of the study group was significantly lower than that of the control group (P<0.05). In conclusion, 3D-DSA combined with neurointerventional thrombolysis can significantly reduce the expression of inflammatory cytokines and improve the quality of life in patients with cerebrovascular occlusion, which has a high clinical value.
Keywords: cerebrovascular occlusion; neurointerventional thrombolysis; three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography; value assessment.
Copyright: © Jiao et al.
Figures
References
-
- Horie N, Tateishi Y, Morikawa M, Morofuji Y, Hayashi K, Izumo T, Tsujino A, Nagata I, Matsuo T. Acute stroke with major intracranial vessel occlusion: characteristics of cardioembolism and atherosclerosis-related in situ stenosis/occlusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;32:24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.12.043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jayaraman MV, Hussain MS, Abruzzo T, Albani B, Albuquerque FC, Alexander MJ, Ansari SA, Arthur AS, Baxter B, Bulsara KR, et al. Embolectomy for stroke with emergent large vessel occlusion (ELVO): Report of the Standards and Guidelines Committee of the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015;7:316–321. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-011717. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
