Botulinum toxin A treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32010269
- PMCID: PMC6966161
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8301
Botulinum toxin A treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
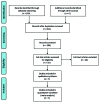
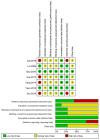
The present meta-analysis study aimed to investigate the safety and efficacy of local administration of botulinum toxin (BTX-A) vs. lidocaine in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. A systematic search of the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang, Chongqing VIP Information Co. and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database was performed to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing BTX-A and lidocaine in the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. The primary outcomes were Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) pain scores at 1, 2 and 3 months after treatment and the effective rate. Secondary outcomes were scores on the McGill pain questionnaire and adverse event rate. A total of 7 RCTs comprising 752 patients were included. The VAS pain score was significantly lower at 1 month [mean difference (MD)=-2.31; 95% CI: -3.06, -1.56; P<0.00001)], 2 months (MD=-2.18; 95% CI: -2.24, -2.11; P<0.00001) and 3 months (MD=-1.93; 95% CI: -3.05, -0.82; P=0.0007) after treatment, the effective rate was significantly higher (odds ratio=2.9; 95% CI: 1.71, 4.13; P<0.0001) and scores on the McGill pain questionnaire were significantly lower (MD=-10.93; 95% CI: -21.02, -0.83; Z=2.12; P=0.03) in patients who received BTX-A for post-herpetic neuralgia compared to those who received lidocaine. There was no difference in the adverse event rate between treatments. In conclusion, BTX-A has potential as a safe and effective treatment option for post-herpetic neuralgia. Further large and well-designed RCTs are required to confirm this conclusion.
Keywords: botulinum toxin-a; efficacy; meta-analysis; post-herpetic neuralgia; safety.
Copyright: © Li et al.
Figures

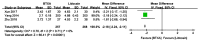
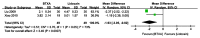

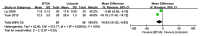
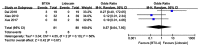
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous injection of botulinum toxin in the treatment of Chinese postherpetic neuralgia compared to analgesics: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1479931. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1479931. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39484052 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin-A for the treatment of neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Pain Res. 2018 Oct 12;11:2343-2351. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S168650. eCollection 2018. J Pain Res. 2018. PMID: 30349359 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in treatment of trigeminal neuralgia and peripheral neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Brain Behav. 2019 Oct;9(10):e01409. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1409. Epub 2019 Sep 21. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 31541518 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of botulinum A toxin for the treatment of chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis.Eur J Pain. 2022 May;26(5):980-990. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1941. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Eur J Pain. 2022. PMID: 35293078
-
[Systematic review and sequential analysis on treatment of herpes zoster pain mainly by fire needle therapy].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Sept 25;44(9):677-85. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190004. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 31532139 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Botulinum toxin type A inhibits microglia pyroptosis by suppressing Cblb-mediated degradation of Pdlim1 to attenuate neuropathic pain.J Headache Pain. 2025 Jul 22;26(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02109-w. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40696327 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin A and Pulsed Radiofrequency on Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 May 30;2022:1579937. doi: 10.1155/2022/1579937. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35685657 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multidimensional Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin in Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;14(5):308. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050308. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weaver BA. The burden of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in the United States. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007;107(Suppl 1):S2–S7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
