Identification of differentially expressed protein-coding genes in lung adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 32010276
- PMCID: PMC6966171
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8300
Identification of differentially expressed protein-coding genes in lung adenocarcinomas
Abstract
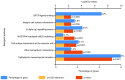
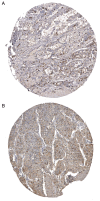
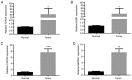
Lung adenocarcinoma accounts for a high proportion of lung cancers. Though efforts have been made to develop new and effective treatments for this disease, the mortality rate remains high. Gene expression microarrays facilitate the study of lung cancer at the molecular level. The present study aimed to detect differentially expressed protein-coding genes to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for lung adenocarcinoma. Aberrations in gene expression in lung adenocarcinoma were determined by analysis of mRNA microarray datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks and statistical analysis were used to identify the biological functions of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The results of the bioinformatics analysis were subsequently validated using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. A total of 303 DEGs were identified in lung adenocarcinomas, and they were enriched in a number of cancer-associated GO terms and KEGG pathways. DNA topoisomerase 2α (TOP2A), cell division cycle protein homolog 20 (CDC20), mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine protein kinase BUB1 (BUB1) and mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2A (MAD2L1) exhibited the highest degree of interaction in the PPI network. Survival analysis performed using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox regression indicated that these four genes were all significantly associated with the survival of patients with lung adenocarcinomas. In conclusion, TOP2A, CDC20, BUB1 and MAD2L1 may be key protein-coding genes that may serve as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: DNA topoisomerase 2α; bioinformatics analysis; biomarkers; cell division cycle protein homolog 20; lung adenocarcinoma; mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine protein kinase BUB1; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2L1.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures





References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. cdc.gov/cancer/lung/statistics/index.htm. [Mar 26;2014 ];Lung Cancer Statistics.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
