Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of Boswellia serrate gum resin in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 32010304
- PMCID: PMC6966228
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8353
Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of Boswellia serrate gum resin in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity
Abstract
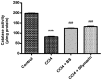
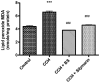
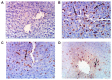
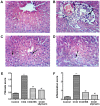
The present study aims to investigate the potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of Boswellia serrate (BS) gum resin against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage. Four groups consisting of eight rats each were designated: Group I, normal healthy control; group II, CCl4-induced liver fibrosis; group III, CCl4-induced liver fibrosis followed by BS treatment daily for two weeks; and group IV, CCl4-induced liver fibrosis followed by silymarin treatment daily for two weeks. Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), interleukin-6 (IL-6), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were assessed, in addition to histopathological and fibrotic changes in liver tissues isolated from the rats. BS significantly ameliorated CCl4-induced increases in serum aspartate (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels, reduced lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activities in addition to restoring total bilirubin, triglyceride and albumin levels. BS treatment also alleviated oxidative stress and improved total antioxidant capacity in the liver, and reduced the expression of TNF-α, NF-κB, TGF-β, IL-6 and COX-2. On a histopathological level, BS treatment also exhibited antifibrotic activity. In conclusion, these findings suggest that BS contains potentially hepatoprotective effects against CCl4-induced liver injury via its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic characteristics.
Keywords: boswellia serrata; cyclooxygenase-2; hepatoprotective; interleukin-6; liver fibrosis; transforming growth factor-β.
Copyright: © Eltahir et al.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Boswellia serrate Gum Resin Mitigates Renal Toxicity: Role of TNF-α, Interleukins, TGF-β, and Lipid Peroxidation.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;14(12):1669. doi: 10.3390/life14121669. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768376 Free PMC article.
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):973-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140589
-
Naringenin prevents experimental liver fibrosis by blocking TGFβ-Smad3 and JNK-Smad3 pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jun 28;23(24):4354-4368. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4354. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28706418 Free PMC article.
-
Myricitrin exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic activity in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated mice.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Mar 25;230:21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.01.030. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25656916
Cited by
-
L-Carnitine ameliorates the liver by regulating alpha-SMA, iNOS, HSP90, HIF-1alpha, and RIP1 expressions of CCL4-toxic rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Feb;24(2):184-190. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2020.47711.10990. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33953857 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing combination treatment with glycyrrhizin and boswellic acids for hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 infection: a randomized clinical trial.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Apr;30(2):477-486. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00939-7. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35233748 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antioxidant Phytoconstituents From Onosma bracteata Wall. (Boraginaceae) Ameliorate the CCl4 Induced Hepatic Damage: In Vivo Study in Male Wistar Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1301. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01301. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32973525 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the hepatoprotective potential of the parasitic plant Orobanche foetida Poir. aqueous extract against CCl4-induced liver injury in rat.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1320062. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1320062. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38239200 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Properties of Frankincense: Implications for Anticancer Therapy.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Aug;30(8):759-767. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-4105-x. Epub 2024 May 31. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 38816637
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
