Attenuation of reserpine-induced fibromyalgia via ROS and serotonergic pathway modulation by fisetin, a plant flavonoid polyphenol
- PMID: 32010308
- PMCID: PMC6966137
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8328
Attenuation of reserpine-induced fibromyalgia via ROS and serotonergic pathway modulation by fisetin, a plant flavonoid polyphenol
Abstract
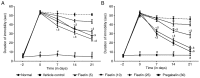
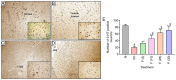
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic complex musculoskeletal disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance, memory defects and mood changes. Fisetin, a plant flavonoid polyphenol, has been reported to possess potent antioxidant, antinociceptive and neuroprotective activities. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of fisetin against reserpine-induced FM (RIF) in rats. RIF was induced in male Wistar rats (180-220 gm) using reserpine (1 mg/kg; subcutaneous; once daily for 3 consecutive days) and the rats were treated with fisetin (5, 10 and 25 mg/kg) for 21 days. Various behavioral, biochemical and molecular parameters were evaluated. Administration of reserpine induced allodynia, hyperalgesia and depression, which were significantly ameliorated (P<0.05) by fisetin (10 and 25 mg/kg), as reflected by an increase in paw and tail withdrawal latency, increased paw withdrawal threshold, and decreased immobility time. Reserpine led to decreased biogenic amine levels [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), noradrenaline (NA) and dopamine (DA)] and increased the ratio to their metabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the spinal cord, thalamus and prefrontal cortex was significantly decreased (P<0.05) by fisetin. Immunohistological analysis of brain tissue revealed that fisetin significantly inhibited (P<0.05) reserpine-induced depletion of 5-HT. It also significantly inhibited (P<0.05) elevated oxido-nitrosative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, as analyzed by flow cytometry in RIF rats. Fisetin exerts its antinociceptive and anti-depressive potential via modulation of decreased levels of biogenic amines (5-HT, NA and DA), elevated oxido-nitrosative stress and ROS to ameliorate allodynia, hyperalgesia, and depression in experimental RIF.
Keywords: 5-HT; FM; NA; ROS; dopamine; fisetin; immunohistochemistry; reserpine.
Copyright: © Yao et al.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
