Evaluation of Flexibility, Microstructure and Elemental Analysis of Some Contemporary Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments
- PMID: 32010393
- PMCID: PMC6986506
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.811
Evaluation of Flexibility, Microstructure and Elemental Analysis of Some Contemporary Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments
Abstract
Background: Contemporary nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary endodontic instruments had a revolutionary impact on the success of root canal treatment.
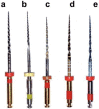
Aim: To evaluate the flexibility, microstructure and elemental analysis of four different recent NiTi rotary instruments, namely; Wave One Gold, TF adaptive, HyFlex EDM and Gr_Reciproc Blue compared to conventional Protaper Universal (F2).
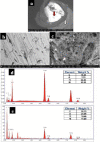
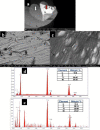
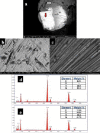
Material and methods: The NiTi rotary files were subjected to cantilever bending test to evaluate their flexibility. The microstructural characteristics and elemental analysis were examined via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDX).
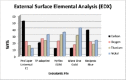
Results: The TF adaptive, HyFlex EDM and Wave One Gold endodontic files showed significantly lower cantilever bending values (i.e., higher flexibility) than Protaper F2 and Gr_Reciproc Blue (p < 0.05). The SEM micrographs showed that the bulk of all examined files showed multiple striations due to the cutting process, on the other hand, their external surfaces were different: The Protaper Universal F2 showed multiple voids, while the TF Adaptive surface exhibited more uniform structure. The Hyflex EDM had a crater-like surface, whereas Wave one Gold showed machining grooves with minimum defects, while Reciproc Blue displayed machining grooves with random scratch lines. There was a significant difference in bulk and surface elemental analysis of the various examined files, yet composed mainly of the same elements.
Conclusion: Chemical composition, heat treatment, manufacturing process and geometrical design of the NiTi rotary instrument have a great influence on their flexibility and microstructure.
Keywords: Elemental analysis; Endodontic files; Flexibility; Heat treatment; Microstructure; NiTi instruments.
Copyright: © 2019 Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Rasha M. Abdelraouf.
Figures




References
-
- Aun DP, Peixoto IFDC, Houmard M, Buono VTL. Enhancement of NiTi superelastic endodontic instruments by TiO2 coating. Materials Science and Engineering C. 2016;68:675–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.031 PMid:27524067. - PubMed
-
- R N. NiTi Endodontics:Contemporary Views Reviewed. Austin Journal of Dentistry. 2018;5:4. https://doi.org/10.26420/austinjdent.2018.1112.
-
- Walid N. Review and Classification of Heat Treatment Procedures of Niti Instruments and Its Implication on Files Fatigue. J Dental Sci. 2017;2(2):1–19.
-
- Aoun CM, Nehme WB, Naaman AS, Khalil IT. Review and Classification of Heat Treatment Procedures and Their Impact on Impact on Mechanical Behavior of Endodontic Files. International Journal of Current Research. 2017;9(5):51300–6.
-
- Viana ACD, Chaves Craveiro, De Melo M, Guiomar De Azevedo Bahia M, Lopes Buono VT. Relationship between flexibility and physical, chemical, and geometric characteristics of rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology. 2010;110(4):527–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.05.006 PMid:20868997. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
