The Prognostic Significance of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Loss in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32010404
- PMCID: PMC6986515
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.757
The Prognostic Significance of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Loss in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to determine the prognostic significance of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) loss in breast cancer.
Methods: We conducted a meta-analysis study. Sample of this study were research articles that evaluated PTEN loss and prognosis in breast cancer patients. We searched for relevant studies published in PubMed and Proquest from January 2010 to July 2018. We reviewed studies that examined the association between immunohistochemical expression of PTEN and breast cancer prognosis using meta-analysis methods. Pooled risk ratios (RR) were calculated using fixed and random-effect models. Data were processed using Review Manager 5.3 (RevMan 5.3).
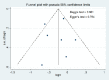
Results: There were 7 studies conducted a systematic review then continued to evaluate the association of PTEN loss and breast cancer prognosis by meta-analysis. There was a significant association of PTEN loss with poor prognosis of breast cancer (RR = 0.76 [95% CI 0.59-0.98 p <0.07), and there was not any significant publication bias for studies included.
Conclusion: This study confirmed PTEN loss is an important independent factor for breast cancer prognosis.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Immunohistochemical; PTEN; Prognosis.
Copyright: © 2019 Indri Windarti, Wirsma Arif Harahap, Ricvan Dana Nindrea, Eti Yerizel, Primariadewi Rustamadji.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RKM, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):29–32. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21254 PMid:25559415. - PubMed
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Globacon. 2012: estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. 2012
-
- Strasser-Weippi K, Horich N, Smith IE, O'Shaughnessy J, Ejlertsen B, Boyle F, et al. Long-term hazard of recurrence in HER2+breast cancer patients untreated with antiHER2 therapy. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-015-0568-1 PMid:25888246 PMCid:PMC4423419. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albayati MR, Alhilfi HS, Almohammadawi KO, Althaalibi SM, et al. An Outcome of Localized HER2 Positive Breast Cancer Treated with Adjuvant Trastuzumab in Clinical Practice:Retrospective Observational Study. Cancer Ther Oncol Int J. 2017;7(3):1–5. https://doi.org/10.19080/CTOIJ.2017.07.555712.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials