Irradiance plays a significant role in photobiomodulation of B16F10 melanoma cells by increasing reactive oxygen species and inhibiting mitochondrial function
- PMID: 32010497
- PMCID: PMC6968738
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.11.000027
Irradiance plays a significant role in photobiomodulation of B16F10 melanoma cells by increasing reactive oxygen species and inhibiting mitochondrial function
Abstract
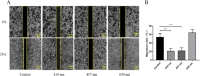
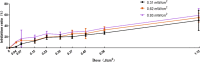
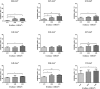
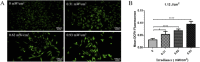
Melanoma is a type of aggressive cancer. Recent studies have indicated that blue light has an inhibition effect on melanoma cells, but the effect of photobiomodulation (PBM) parameters on the treatment of melanoma remains unknown. Thus, this study was aimed to investigate B16F10 melanoma cells responses to PBM with varying irradiance and doses, and further explored the molecular mechanism of PBM. Our results suggested that the responses of B16F10 melanoma cells to PBM with varying irradiance and dose were different and the inhibition of blue light on cells under high irradiance was better than low irradiance at a constant total dose (0.04, 0.07, 0.15, 0.22, 0.30, 0.37, 0.45, 0.56 or 1.12 J/cm2), presumably due to that high irradiance can produce more ROS, thus disrupting mitochondrial function.
© 2019 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of gene expression patterns on B16F10 melanoma cells under Photobiomodulation of different light modes.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021 Mar;216:112127. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112127. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021. PMID: 33517070
-
The pulse light mode enhances the effect of photobiomodulation on B16F10 melanoma cells through autophagy pathway.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Feb 15;38(1):71. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03733-1. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36790539
-
The review of the light parameters and mechanisms of Photobiomodulation on melanoma cells.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022 Jan;38(1):3-11. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12715. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022. PMID: 34181781 Review.
-
Responses of melanoma cells to photobiomodulation depend on cell pigmentation and light parameters.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2022 Oct;235:112567. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112567. Epub 2022 Sep 13. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2022. PMID: 36115314
-
Low-level laser therapy/photobiomodulation in the management of side effects of chemoradiation therapy in head and neck cancer: part 2: proposed applications and treatment protocols.Support Care Cancer. 2016 Jun;24(6):2793-805. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3153-y. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Support Care Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26984249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of photobiomodulation therapy in oncology: A systematic review.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(22):8279-8300. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3582. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 33107198 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Narrow-Band Imaging as a Novel Light Source for Photodynamic Therapy for Superficial Cancers via Endoscopes.Gastroenterology Res. 2024 Apr;17(2):72-81. doi: 10.14740/gr1694. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Gastroenterology Res. 2024. PMID: 38716285 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Lipopeptides as Selective Anticancer Agents: In vitro Efficacy on B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(12):873-882. doi: 10.2174/0118715206351208250102114944. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39851102
-
Lightwave-reinforced stem cells with enhanced wound healing efficacy.J Tissue Eng. 2021 Dec 18;12:20417314211067004. doi: 10.1177/20417314211067004. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2021. PMID: 34987748 Free PMC article.
-
Reviewing the efficiency of photobiomodulation therapy in oncological treatment.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 8;14:1447653. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1447653. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39439950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
