Multiplex protein-specific microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation
- PMID: 32010503
- PMCID: PMC6968765
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.11.000099
Multiplex protein-specific microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation
Abstract
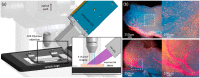
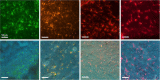
Immunohistochemical techniques, such as immunofluorescence (IF) staining, enable microscopic imaging of local protein expression within tissue samples. Molecular profiling enabled by IF is critical to understanding pathogenesis and is often involved in complex diagnoses. A recent innovation, known as microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation (MUSE), uses deep ultraviolet (≈280 nm) illumination to excite labels at the tissue surface, providing equivalent images without fixation, embedding, and sectioning. However, MUSE has not yet been integrated into traditional IF pipelines. This limits its application in more complex diagnoses that rely on protein-specific markers. This paper aims to broaden the applicability of MUSE to multiplex immunohistochemistry using quantum dot nanoparticles. We demonstrate the advantages of quantum dot labels for protein-specific MUSE imaging on both paraffin-embedded and intact tissue, significantly expanding MUSE applicability to protein-specific applications. Furthermore, with recent innovations in three-dimensional ultraviolet fluorescence microscopy, this opens the door to three-dimensional IF imaging with quantum dots using ultraviolet excitation.
© 2019 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Castillo-Carranza D. L., Nilson A. N., Van Skike C. E., Jahrling J. B., Patel K., Garach P., Gerson J. E., Sengupta U., Abisambra J., Nelson P., Troncoso J., Ungvari Z., Galvan V., Kayed R., “Cerebral microvascular accumulation of tau oligomers in alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies,” Aging Dis. 8(3), 257–266 (2017).10.14336/AD.2017.0112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fereidouni F., Harmany Z. T., Tian M., Todd A., Kintner J. A., McPherson J. D., Borowsky A. D., Bishop J., Lechpammer M., Demos S. G., Levenson R., “Microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation for rapid slide-free histology,” Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1(12), 957–966 (2017).10.1038/s41551-017-0165-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xie W., Chen Y., Wang Y., Wei L., Yin C., Glaser A. K., Fauver M. E., Seibel E. J., Dintzis S. M., Vaughan J. C., Reder N. P., Liu J. T. C., “Microscopy with ultraviolet surface excitation for wide-area pathology of breast surgical margins,” J. Biomed. Opt. 24(02), 1 (2019).10.1117/1.JBO.24.2.026501 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
