Quantitative Intracellular pH Determinations in Single Live Mammalian Spermatozoa Using the Ratiometric Dye SNARF-5F
- PMID: 32010689
- PMCID: PMC6978660
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00366
Quantitative Intracellular pH Determinations in Single Live Mammalian Spermatozoa Using the Ratiometric Dye SNARF-5F
Abstract
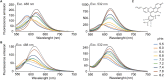
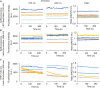
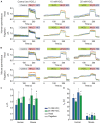
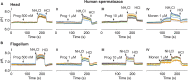
Intracellular pH (pH i ) plays a crucial role in mammalian sperm physiology. However, it is a challenging task to acquire quantitative single sperm pH i images due to their small size and beating flagella. In this study, we established a robust pH i imaging system using the dual-emission ratiometric pH indicator, SNARF-5F. Simultaneous good signal/noise ratio fluorescence signals were obtained exciting with a green high-power LED (532 nm) and acquiring with an EM-CCD camera through an image splitter with two band-pass filters (550-600 nm, channel 1; 630-650 nm, channel 2). After in vivo calibration, we established an imaging system that allows determination of absolute pH i values in spermatozoa, minimizing cell movement artifacts. Using this system, we determined that bicarbonate increases non-capacitated human pH i with slower kinetics than in mouse spermatozoa. This difference suggests that distinct ionic transporters might be involved in the bicarbonate influx into human and mouse spermatozoa. Alternatively, pH i regulation downstream bicarbonate influx into spermatozoa could be different between the two species.
Keywords: alkalization; dual emission; image splitter; intracellular pH; ratiometric; spermatozoa.
Copyright © 2020 Chávez, Darszon, Treviño and Nishigaki.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hyperpolarization induces cytosolic alkalization of mouse sperm flagellum probably through sperm Na+/H+ exchanger.Reproduction. 2022 Aug 24;164(4):125-134. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0101. Print 2022 Oct 1. Reproduction. 2022. PMID: 35900329
-
Are there intracellular Ca2+ oscillations correlated with flagellar beating in human sperm? A three vs. two-dimensional analysis.Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 Sep 1;23(9):583-593. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gax039. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28911211
-
Determination of intracellular pH in phytoplankton using the fluorescent probe, SNARF, with detection by fluorescence spectroscopy.J Microbiol Methods. 2018 Sep;152:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2018.07.023. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Microbiol Methods. 2018. PMID: 30077695
-
Digital image analysis of flagellar beating and microtubule sliding of activated and hyperactivated sperm flagella.Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl. 2007;65:327-30. Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17644972 Review.
-
Roles of intracellular cyclic AMP signal transduction in the capacitation and subsequent hyperactivation of mouse and boar spermatozoa.J Reprod Dev. 2013 Oct;59(5):421-30. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2013-056. J Reprod Dev. 2013. PMID: 24162806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Starvation induces an increase in intracellular calcium and potentiates the progesterone-induced mouse sperm acrosome reaction.FASEB J. 2021 Apr;35(4):e21528. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100122R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33742713 Free PMC article.
-
A Minimal Model Shows that a Positive Feedback Loop Between sNHE and SLO3 can Control Mouse Sperm Capacitation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 25;10:835594. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.835594. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35399518 Free PMC article.
-
Driving electrochemical reactions at the microscale using CMOS microelectrode arrays.Lab Chip. 2023 Nov 21;23(23):5047-5058. doi: 10.1039/d3lc00630a. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 37916299 Free PMC article.
-
Mis-splicing of a neuronal microexon promotes CPEB4 aggregation in ASD.Nature. 2025 Jan;637(8045):496-503. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08289-w. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39633052 Free PMC article.
-
An ion transporter in sperm that has features of a channel.Nature. 2023 Nov;623(7985):38-40. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-03154-8. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37880527 No abstract available.
References
-
- Babcock D. F. (1983). Examination of the intracellular ionic environment and of ionophore action by null point measurements employing the fluorescein chromophore. J. Biol. Chem. 258 6380–6389. - PubMed
-
- Balderas E., Sánchez-Cárdenas C., Chávez J. C., De La Vega Beltrán J. L., Gómez-Lagunas F., Treviño C. L., et al. (2013). The anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib inhibits t-type Ca2+ currents in spermatogenic cells yet it elicits the acrosome reaction in mature sperm. FEBS Lett. 587 2412–2419. 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.05.068 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

