Development of Indirect Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Lateral-Flow Immunochromatographic Strip for the Detection of Digoxin in Human Blood
- PMID: 32010807
- PMCID: PMC6990433
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02254
Development of Indirect Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Lateral-Flow Immunochromatographic Strip for the Detection of Digoxin in Human Blood
Abstract
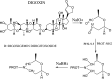
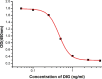
Mouse-mouse hybridoma cell lines producing stable, highly specific monoclonal antibodies with good affinity for the cardiac glycoside digoxin (DIG) were established to construct an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and lateral-flow immunochromatographic strip to detect DIG in human blood. The hapten DIG was coupled to bovine serum albumin or chicken ovalbumin by sodium periodate oxidation. The highest sensitivity and specificity antibody had a median inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.45 ng/mL, a linear range of detection of 0.293-0.7 ng/mL, and low cross-reactivity with several DIG analogues. The cut-off value of the lateral-flow immunochromatographic strip was 5 ng/mL when the strip was tested with human blood. The immunochromatographic lateral flow strip test provides a quick and convenient method for determining DIG in plasma which can be visually observed in only 5 min to promote rational drug use.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lam P. H.; Bhyan P.; Arundel C.; Dooley D. J.; Sheriff H. M.; Mohammed S. F.; et al. Digoxin use and lower risk of 30-day all-cause readmission in older patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction receiving beta-blockers. Clin. Cardiol. 2018, 41, 406–412. 10.1002/clc.22889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
