Oscillating diffusion-encoding with a high gradient-amplitude and high slew-rate head-only gradient for human brain imaging
- PMID: 32011027
- PMCID: PMC7180099
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28180
Oscillating diffusion-encoding with a high gradient-amplitude and high slew-rate head-only gradient for human brain imaging
Abstract
Purpose: We investigate the importance of high gradient-amplitude and high slew-rate on oscillating gradient spin echo (OGSE) diffusion imaging for human brain imaging and evaluate human brain imaging with OGSE on the MAGNUS head-gradient insert (200 mT/m amplitude and 500 T/m/s slew rate).
Methods: Simulations with cosine-modulated and trapezoidal-cosine OGSE at various gradient amplitudes and slew rates were performed. Six healthy subjects were imaged with the MAGNUS gradient at 3T with OGSE at frequencies up to 100 Hz and b = 450 s/mm2 . Comparisons were made against standard pulsed gradient spin echo (PGSE) diffusion in vivo and in an isotropic diffusion phantom.
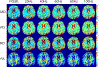
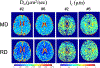
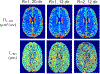
Results: Simulations show that to achieve high frequency and b-value simultaneously for OGSE, high gradient amplitude, high slew rates, and high peripheral nerve stimulation limits are required. A strong linear trend for increased diffusivity (mean: 8-19%, radial: 9-27%, parallel: 8-15%) was observed in normal white matter with OGSE (20 Hz to 100 Hz) as compared to PGSE. Linear fitting to frequency provided excellent correlation, and using a short-range disorder model provided radial long-term diffusivities of D∞,MD = 911 ± 72 µm2 /s, D∞,PD = 1519 ± 164 µm2 /s, and D∞,RD = 640 ± 111 µm2 /s and correlation lengths of lc,MD = 0.802 ± 0.156 µm, lc,PD = 0.837 ± 0.172 µm, and lc,RD = 0.780 ± 0.174 µm. Diffusivity changes with OGSE frequency were negligible in the phantom, as expected.
Conclusion: The high gradient amplitude, high slew rate, and high peripheral nerve stimulation thresholds of the MAGNUS head-gradient enables OGSE acquisition for in vivo human brain imaging.
Keywords: diffusion imaging; head-gradient; microstructure.
© 2020 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

