The prevalence of first-onset temporomandibular disorder in low back pain and associated risk factors: A nationwide population-based cohort study with a 15-year follow-up
- PMID: 32011444
- PMCID: PMC7220485
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018686
The prevalence of first-onset temporomandibular disorder in low back pain and associated risk factors: A nationwide population-based cohort study with a 15-year follow-up
Abstract
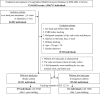
The coexistence of low back pain (LBP) and temporomandibular disorder (TMD) has often been noted clinically. However, studies of the association between these two conditions involving a large population with longitudinal evidences are lacking. Therefore, the study aimed to investigate the association between LBP and TMD in a nationwide-matched cohort population with a 15-year follow-up.Data of 65,121 patients newly diagnosed with LBP were analyzed, along with those of 195,363 (1:3) sex- and age-matched controls. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to determine TMD risk between the LBP and non-LBP groups. Kaplan-Meier method was used for determining the cumulative risk of first-onset TMD between groups, with a 15-year follow-up.The LBP group was more likely to develop first-onset TMD (adjusted hazards ratio (HR) = 1.561, P < .001), after adjusting for demographic variables and comorbidities. The risk factors for TMD were LBP, young age, higher insured premium, and osteoporosis. In the subgroup analysis, the LBP group had a higher risk of TMD than the non-LBP group in all stratifications.LBP is the risk factor contributing to the development of first-onset TMD. Therefore, clinicians should be reminded to manage LBP disorders concurrently when treating TMD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Gonçalves DA, Dal Fabbro AL, Campos JA, et al. Symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in the population: an epidemiological study. J Orofac Pain 2010;24:270–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

