Effect of isolation practice on the transmission of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus among hemodialysis patients: A 2-year prospective cohort study
- PMID: 32011472
- PMCID: PMC7220504
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018782
Effect of isolation practice on the transmission of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus among hemodialysis patients: A 2-year prospective cohort study
Abstract
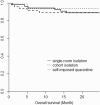
Hemodialysis (HD) patients had a high rate of infection transmission and mortality during the middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) outbreak in Saudi Arabia. A standardized guideline on isolation technique for exposed HD patients is not available. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of different isolation strategies on the prevention of secondary viral transmission and clinical outcomes among exposed HD patients.During the 2015 MERS-CoV outbreak in Korea, 116 patients in 3 HD units were incidentally exposed to individuals with confirmed MERS-CoV infection and underwent different types of isolation, which were as follows: single-room isolation (n = 54, 47%), cohort isolation (n = 46, 40%), and self-imposed quarantine (n = 16, 13%). The primary outcome was rate of secondary viral transmission. The secondary outcome measures were changes in clinical and biochemical markers during the isolation period, difference in clinical and biochemical markers according to the types of isolation practice, and effect of isolation practice on patient survival.During a mean isolation period of 15 days, no further cases of secondary transmission were detected among HD patients. Plasma hemoglobin, serum calcium, and serum albumin levels and single-pool Kt/V decreased during the isolation period but normalized thereafter. Patients who were subjected to self-imposed quarantine had higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure, lower total cholesterol level, and lower Kt/V than those who underwent single-room or cohort isolation. During the 24-month follow-up period, 12 patients died. However, none of the deaths occurred during the isolation period, and no differences were observed in patient survival rate according to different isolation strategies.Although 116 participants in 3 HD units were incidentally exposed to MERS-CoV during the 2015 outbreak in Korea, strict patient surveillance and proper isolation practice prevented secondary transmission of the virus. Thus, a renal disaster protocol, which includes proper contact surveillance and isolation practice, must be established in the future to accommodate the needs of HD patients during disasters or outbreaks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy: 2015 update. Am J Kidney Dis 2015;66:884–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

