Comparison of corneal thickness in patients with dry eye disease using the Pentacam rotating Scheimpflug camera and anterior segment optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 32012201
- PMCID: PMC6996840
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228567
Comparison of corneal thickness in patients with dry eye disease using the Pentacam rotating Scheimpflug camera and anterior segment optical coherence tomography
Abstract
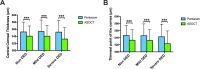
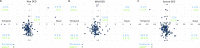
The purpose of this study was to compare central corneal thickness, thinnest corneal thickness, and the thinnest point of the cornea between Pentacam and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (ASOCT) in patients with dry eye disease (DED). This cross-sectional study included 195 participants between November 2015-June 2017. DED was diagnosed using the Asia Dry Eye Society criteria and further divided into mild and severe DED based on kerato-conjunctival vital staining. Central corneal thickness, thinnest corneal thickness, and the thinnest point of the cornea measured by Pentacam and ASOCT were compared, and Pearson's correlation coefficients were estimated. The differences in central corneal thickness and the thinnest corneal thickness between Pentacam and ASOCT were analysed using Bland-Altman and multivariate regression analyses adjusted for age and sex. This study included 70 non-DED subjects and 52 patients with mild and 73 with severe DED. The Pentacam and ASOCT measurements of central corneal thickness and thinnest corneal thickness were strongly correlated, but the respective values were higher when measured with Pentacam. The Bland-Altman analysis revealed differences in central corneal thickness (non DED, 11.8; mild DED, 13.2; severe DED, 19.6) and in thinnest corneal thickness (non DED, 13.1; mild DED, 13.4; severe DED, 20.7). After adjusting for age and sex, the differences in central corneal thickness (β = 7.029 μm, 95%CI 2.528-11.530) and thinnest corneal thickness (β = 6.958 μm, 95%CI 0.037-13.879) were significantly increased in the severe-DED group. The distribution of the thinnest point of the cornea in the cornea's inferior temporal quadrant between Pentacam and ASOCT deviated in severe DED (Pentacam: 90.4% vs. ASOCT: 83.6%). Clinicians should consider that there were significant differences in corneal-morphology assessment between the measurements with Pentacam and ASOCT in severe DED.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Grewal DS, Brar GS, Grewal SP. Assessment of central corneal thickness in normal, keratoconus, and post-laser in situ keratomileusis eyes using Scheimpflug imaging, spectral domain optical coherence tomography, and ultrasound pachymetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(6):954–64. Epub 2010/05/25. 10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.12.033 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

