Potentilla rugulosa Nakai Extract Attenuates Bisphenol A-, S- and F-Induced ROS Production and Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes in the Absence of Dexamethasone
- PMID: 32012803
- PMCID: PMC7071078
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9020113
Potentilla rugulosa Nakai Extract Attenuates Bisphenol A-, S- and F-Induced ROS Production and Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes in the Absence of Dexamethasone
Abstract
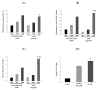
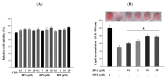
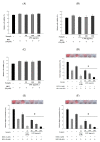
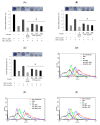
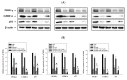
Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) disrupt the physiological metabolism, thus playing an important role in the development of obesity. EDCs, the so-called 'obesogens', might predispose some individuals to gain weight. This study investigated the effects of bisphenol A (BPA) and its alternatives (BPS and BPF) on adipocyte differentiation and the effects of the leaves of Potentilla rugulosa Nakai extract (LPE) as a functional food ingredient on obesogen-induced lipid production and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. The results showed that LPE has high total phenolic and flavonoid contents (77.58 ± 0.57 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g and 57.31 ± 1.72 mg quercetin equivalents (QE)/g, respectively). In addition, LPE exerted significant antioxidant effects in terms of DPPH radical scavenging activity, reducing power, ferric-ion reducing antioxidant power, and oxygen radical absorbance capacity. BPA, BPS, and BPF increased lipid accumulation, protein expressions of adipogenic transcription factors (PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and aP2), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in 3T3-L1 cells. However, LPE suppressed the BPA-, BPS-, and BPF-induced effects on adipogenesis. Therefore, LPE has potential as a functional food supplement that can prevent bisphenol-induced lipid metabolism disorders.
Keywords: Lipid metabolism disorders; Potentilla rugulosa Nakai; ROS production; bisphenol A; endocrine disrupting chemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this study.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

