Wearable Emotion Recognition Using Heart Rate Data from a Smart Bracelet
- PMID: 32012920
- PMCID: PMC7038485
- DOI: 10.3390/s20030718
Wearable Emotion Recognition Using Heart Rate Data from a Smart Bracelet
Abstract
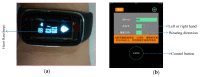
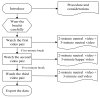
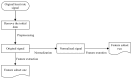
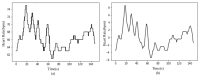
Emotion recognition and monitoring based on commonly used wearable devices can play an important role in psychological health monitoring and human-computer interaction. However, the existing methods cannot rely on the common smart bracelets or watches for emotion monitoring in daily life. To address this issue, our study proposes a method for emotional recognition using heart rate data from a wearable smart bracelet. A 'neutral + target' pair emotion stimulation experimental paradigm was presented, and a dataset of heart rate from 25 subjects was established, where neutral plus target emotion (neutral, happy, and sad) stimulation video pairs from China's standard Emotional Video Stimuli materials (CEVS) were applied to the recruited subjects. Normalized features from the data of target emotions normalized by the baseline data of neutral mood were adopted. Emotion recognition experiment results approved the effectiveness of 'neutral + target' video pair simulation experimental paradigm, the baseline setting using neutral mood data, and the normalized features, as well as the classifiers of Adaboost and GBDT on this dataset. This method will promote the development of wearable consumer electronic devices for monitoring human emotional moods.
Keywords: emotion recognition; heart rate; smart bracelet; wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Gouizi K., Maaoui C., Reguig F.B. Negative emotion detection using EMG signal; Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT); Metz, France. 3–5 November 2014; pp. 690–695.
-
- Khetrapal N. Detection of Negative Emotions in Autistics: Questioning the ‘Amygdala Hypothesis’. New Sch. Psychol. Bull. 2007;5:968–977.
-
- Bailenson J.N., Pontikakis E.D., Mauss I.B., Gross J.J., Jabon M.E., Hutcherson C.A., Nass C., John O. Real-time classification of evoked emotions using facial feature tracking and physiological responses. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2008;66:303–317. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhcs.2007.10.011. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

