Deep Eutectic Solvents as Effective Reaction Media for the Synthesis of 2-Hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole-based Scaffolds en Route to Donepezil-Like Compounds
- PMID: 32013037
- PMCID: PMC7037276
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030574
Deep Eutectic Solvents as Effective Reaction Media for the Synthesis of 2-Hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole-based Scaffolds en Route to Donepezil-Like Compounds
Abstract
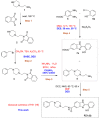
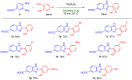
An unsubstituted 2-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole has recently been included as a scaffold in a series of hybrids (including the hit compound PZ1) based on the framework of the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor Donepezil, which is a new promising multi-target ligand in Alzheimer's disease (AD) treatment. Building upon these findings, we have now designed and completed the whole synthesis of PZ1 in the so-called deep eutectic solvents (DESs), which have emerged as an unconventional class of bio-renewable reaction media in green synthesis. Under optimized reaction conditions, the preparation of a series of 2-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole-based nuclei has also been perfected in DESs, and comparison with other routes which employ toxic and volatile organic solvents (VOCs) provided. The functionalization of the aromatic ring can have implications on some important biological properties of the described derivatives and will be the subject of future studies of structure-activity relationships (SARs).
Keywords: 2-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole; Alzheimer’s disease; deep eutectic solvents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Piemontese L., Loiodice F., Chaves S., Santos M.A. The Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease: Towards a New Generation of Drugs. Front. Clin. Drug Res. Alzheimer Disord. 2019;8:33–80.
-
- Fiest K.M., Roberts J.I., Maxwell C.J., Hogan D.B., Smith E.E., Frolkis A., Cohen A., Kirk A., Pearson D., Pringsheim T., et al. The prevalence and incidence of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016;43:S51–S82. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2016.36. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous