Bioenergetics and Biomechanics of Handcycling at Submaximal Speeds in Athletes with a Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 32013128
- PMCID: PMC7077182
- DOI: 10.3390/sports8020016
Bioenergetics and Biomechanics of Handcycling at Submaximal Speeds in Athletes with a Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
Background: A study aimed at comparing bioenergetics and biomechanical parameters between athletes with tetraplegia and paraplegia riding race handbikes at submaximal speeds in ecological conditions.
Methods: Five athletes with tetraplegia (C6-T1, 43 ± 6 yrs, 63 ± 14 kg) and 12 athletes with paraplegia (T4-S5, 44 ± 7 yrs, 72 ± 12 kg) rode their handbikes at submaximal speeds under metabolic measurements. A deceleration method (coasting down) was applied to calculate the rolling resistance and frontal picture of each participant was taken to calculate air resistance. The net overall Mechanical Efficiency (Eff) was calculated by dividing external mechanical work to the corresponding Metabolic Power.
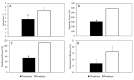
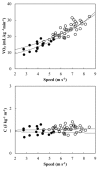
Results: Athletes with tetraplegia reached a lower aerobic speed (4.7 ± 0.6 m s-1 vs. 7.1 ± 0.9 m s-1, P = 0.001) and Mechanical Power (54 ± 15 W vs. 111 ± 25 W, P = 0.001) compared with athletes with paraplegia. The metabolic cost was around 1 J kg-1 m-1 for both groups. The Eff values (17 ± 2% vs. 19 ± 3%, P = 0.262) suggested that the handbike is an efficient assisted locomotion device.
Conclusion: Handbikers with tetraplegia showed lower aerobic performances but a similar metabolic cost compared with handbikers with paraplegia at submaximal speeds in ecological conditions.
Keywords: handbike; locomotion; paralympic classification; paralympic sport; performance.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of crank position and backrest inclination on shoulder load and mechanical efficiency during handcycling.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014 Apr;24(2):386-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2012.01524.x. Epub 2012 Sep 19. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014. PMID: 22989023
-
Determinants of handbike use in persons with spinal cord injury: results of a community survey in Switzerland.Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(1):81-6. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1024339. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 25784201
-
Peak and submaximal steady-state metabolic and cardiorespiratory responses during arm-powered and arm-trunk-powered handbike ergometry in able-bodied participants.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012 Mar;112(3):983-9. doi: 10.1007/s00421-011-2051-8. Epub 2011 Jun 30. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21717120 Clinical Trial.
-
Is handcycling performance affected by hand function impairment? A cross-sectional study on paracycling classification.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025 May 3:1-9. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2025.2492369. Online ahead of print. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2025. PMID: 40319336 Review.
-
Classification in para sport for athletes following cervical spine trauma.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;158:371-377. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63954-7.00035-5. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30482365 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomechanics of elite handcyclists are highly individual-a case series on kinetics, kinematics, and muscular activity.Front Sports Act Living. 2025 May 23;7:1581301. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1581301. eCollection 2025. Front Sports Act Living. 2025. PMID: 40485922 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Relationship between Selected Factors and Stress-Coping Strategies in Handcyclists-A Preliminary Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Apr 27;56(5):211. doi: 10.3390/medicina56050211. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32349214 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Researching Sports Biomechanics for Disabled People".Sports (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;9(12):161. doi: 10.3390/sports9120161. Sports (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakkum A.J., de Groot S., Stolwijk-Swüste J.M., ALLRISC. van Kuppevelt D.J., van der Woude L.H., Janssen T.W. Effects of hybrid cycling versus handcycling on wheelchair-specific fitness and physical activity in people with long-term spinal cord injury: a 16-week randomized controlled trial. Spinal Cord. 2015;53:395–401. doi: 10.1038/sc.2014.237. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Janssen T.W., Dallmeijer A.J., van der Woude L.H. Physical capacity and race performance of handcycle users. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2001;38:33–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

