Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Properties of Carthamus Tinctorius, Hydroxy Safflor Yellow A, and Safflor Yellow A
- PMID: 32013224
- PMCID: PMC7070856
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9020119
Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Properties of Carthamus Tinctorius, Hydroxy Safflor Yellow A, and Safflor Yellow A
Abstract
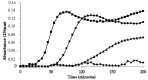
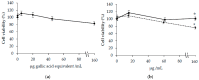
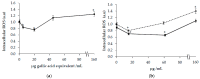
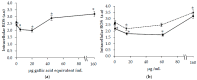
(1) Carthamus Tinctorius L. (safflower) is extensively used in traditional herbal medicine. (2) The aim of this study was to investigate the bioactive properties of polyphenol extracts from flowers of Carthamus Tinctorius (CT) cultivated in Italy. We also evaluated the properties of two bioactive water-soluble flavonoid compounds, hydroxy safflor yellow A (HSYA) and safflor yellow A (SYA), contained in Carthamus Tinctorius petals. (3) The total polyphenol content was 3.5 ± 0.2 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE)/100 g, flavonoids content was 330 ± 23 mg catechin equivalent (CE)/100 g in the flowers. The extract showed a high antioxidant activity evaluated by oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) and 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging assays. In addition, flower extract, SYA, and HSYA were able to reduce the susceptibility of low-density lipoprotein to copper-induced lipid peroxidation. In order to investigate the bioactive properties of flower extract, SYA, and HSYA we also studied their modulatory effect of oxidative stress on human dermal fibroblasts (HuDe) oxidized by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BOOH). The CT extract at concentrations ranging from 0.01-20 mg GAE/mL of polyphenols, exerted a protective effect against t-BOOH triggered oxidative stress. At higher concentration the extract exerted a pro-oxidant effect. Similar results have been obtained using HSYA and SYA. (4) These results demonstrate a biphasic effect exerted by HSYA, SYA, and flower extracts on oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variation in phenolic composition and antioxidant activity during flower development of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.).J Agric Food Chem. 2011 May 11;59(9):4455-63. doi: 10.1021/jf1049936. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21434653
-
De Novo Sequencing and Analysis of the Safflower Transcriptome to Discover Putative Genes Associated with Safflor Yellow in Carthamus tinctorius L.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Oct 26;16(10):25657-77. doi: 10.3390/ijms161025657. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26516840 Free PMC article.
-
Composition of major quinochalcone hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B is associated with colour of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) during colour-transition but not with overall antioxidant capacity: A study on 144 cultivars.Food Res Int. 2022 Dec;162(Pt B):112098. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112098. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36461404
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology and medicinal properties of Carthamus tinctorius L.Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):153-9. doi: 10.1007/s11655-013-1354-5. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Chin J Integr Med. 2013. PMID: 23371463 Review.
-
Hydroxysafflor Yellow A: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for a Broad Spectrum of Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Sep 25;2018:8259280. doi: 10.1155/2018/8259280. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30356354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Simulated In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion on the Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, and Biological Activity of Thymbra spicata L. Extracts.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 9;11(9):1778. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091778. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139852 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 29;11:01265. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01265. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33117148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 11;18(5):710. doi: 10.3390/ph18050710. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Densitometric Quantification and Optimization of Polyphenols in Phyllanthus maderaspatensis by HPTLC.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar;29(3):1521-1529. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.019. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280567 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the photoprotective and antioxidant potential of an avobenzone derivative.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 29;15:1347414. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1347414. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38487263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bukhari I.A. The central analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of the methanolic extract of Carthamus oxycantha. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013;64:369–375. - PubMed
-
- Kim E.O., Oh J.H., Lee S.K., Lee J.Y., Choi S.W. (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seeds. Antioxidant properties and quantification of phenolic compounds from safflower. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007;16:71–77.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

