Reduced miR-26b Expression in Megakaryocytes and Platelets Contributes to Elevated Level of Platelet Activation Status in Sepsis
- PMID: 32013235
- PMCID: PMC7036890
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21030866
Reduced miR-26b Expression in Megakaryocytes and Platelets Contributes to Elevated Level of Platelet Activation Status in Sepsis
Abstract
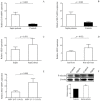
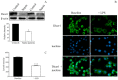
In sepsis, platelets may become activated via toll-like receptors (TLRs), causing microvascular thrombosis. Megakaryocytes (MKs) also express these receptors; thus, severe infection may modulate thrombopoiesis. To explore the relevance of altered miRNAs in platelet activation upon sepsis, we first investigated sepsis-induced miRNA expression in platelets of septic patients. The effect of abnormal Dicer level on miRNA expression was also evaluated. miRNAs were profiled in septic vs. normal platelets using TaqMan Open Array. We validated platelet miR-26b with its target SELP (P-selectin) mRNA levels and correlated them with clinical outcomes. The impact of sepsis on MK transcriptome was analyzed in MEG-01 cells after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment by RNA-seq. Sepsis-reduced miR-26b was further studied using Dicer1 siRNA and calpain inhibition in MEG-01 cells. Out of 390 platelet miRNAs detected, there were 121 significantly decreased, and 61 upregulated in sepsis vs. controls. Septic platelets showed attenuated miR-26b, which were associated with disease severity and mortality. SELP mRNA level was elevated in sepsis, especially in platelets with increased mean platelet volume, causing higher P-selectin expression. Downregulation of Dicer1 generated lower miR-26b with higher SELP mRNA, while calpeptin restored miR-26b in MEG-01 cells. In conclusion, decreased miR-26b in MKs and platelets contributes to an increased level of platelet activation status in sepsis.
Keywords: MEG-01; SELP; inflammation; megakaryocyte; microRNA; platelet activation; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hyperglycaemia suppresses microRNA expression in platelets to increase P2RY12 and SELP levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Feb 28;117(3):529-542. doi: 10.1160/TH16-04-0322. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27975100
-
miR-15a-5p regulates expression of multiple proteins in the megakaryocyte GPVI signaling pathway.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Mar;17(3):511-524. doi: 10.1111/jth.14382. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30632265 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of regulatory platelet microRNAs in patients with sickle cell disease.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 12;8(4):e60932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060932. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593351 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in platelet production and activation.Blood. 2011 May 19;117(20):5289-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-292011. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21364189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Platelet Physiology and Function.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2016 Apr;42(3):215-22. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1570077. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2016. PMID: 26951501 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights Into Platelet-Derived MicroRNAs in Cardiovascular and Oncologic Diseases: Potential Predictor and Therapeutic Target.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 9;9:879351. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.879351. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35757325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes and MicroRNAs: key modulators of macrophage polarization in sepsis pathophysiology.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 17;30(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02561-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40247413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technically Challenging Percutaneous Interventions of Chronic Total Occlusions Are Associated with Enhanced Platelet Activation.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 29;12(21):6829. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216829. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959293 Free PMC article.
-
Heme cytotoxicity is the consequence of endoplasmic reticulum stress in atherosclerotic plaque progression.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89713-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001932 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant long non-coding RNA cancer susceptibility 15 (CASC15) plays a diagnostic biomarker and regulates inflammatory reaction in neonatal sepsis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):10373-10381. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1996514. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34870560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akinosoglou K., Theodoraki S., Xanthopoulou I., Perperis A., Gkavogianni T., Pistiki A., Giamarellos-Bourboulis E., Gogos C.A. Platelet reactivity in sepsis syndrome: Results from the PRESS study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017;36:2503–2512. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-3093-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

