Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-3 Regulates Regeneration in Planarians
- PMID: 32013251
- PMCID: PMC7038108
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21030875
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-3 Regulates Regeneration in Planarians
Abstract
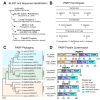
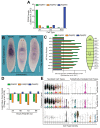
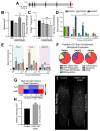
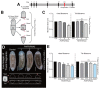
Protein ADP-ribosylation is a reversible post-translational modification (PTM) process that plays fundamental roles in cell signaling. The covalent attachment of ADP ribose polymers is executed by PAR polymerases (PARP) and it is essential for chromatin organization, DNA repair, cell cycle, transcription, and replication, among other critical cellular events. The process of PARylation or polyADP-ribosylation is dynamic and takes place across many tissues undergoing renewal and repair, but the molecular mechanisms regulating this PTM remain mostly unknown. Here, we introduce the use of the planarian Schmidtea mediterranea as a tractable model to study PARylation in the complexity of the adult body that is under constant renewal and is capable of regenerating damaged tissues. We identified the evolutionary conservation of PARP signaling that is expressed in planarian stem cells and differentiated tissues. We also demonstrate that Smed-PARP-3 homolog is required for proper regeneration of tissues in the anterior region of the animal. Furthermore, our results demonstrate, Smed-PARP-3(RNAi) disrupts the timely location of injury-induced cell death near the anterior facing wounds and also affects the regeneration of the central nervous system. Our work reveals novel roles for PARylation in large-scale regeneration and provides a simplified platform to investigate PARP signaling in the complexity of the adult body.
Keywords: PARP; apoptosis; neoblasts; planarians; regeneration; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Akt signaling pathway is required for tissue maintenance and regeneration in planarians.BMC Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 11;16:7. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0107-z. BMC Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27068018 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose): PARadigms and PARadoxes.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1046-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23290998 Review.
-
Planarian PTEN homologs regulate stem cells and regeneration through TOR signaling.Dis Model Mech. 2008 Sep-Oct;1(2-3):131-43; discussion 141. doi: 10.1242/dmm.000117. Epub 2008 Sep 18. Dis Model Mech. 2008. PMID: 19048075 Free PMC article.
-
Regeneration and maintenance of the planarian midline is regulated by a slit orthologue.Dev Biol. 2007 Jul 15;307(2):394-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.006. Epub 2007 May 22. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17553481 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) signaling in cell death.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1153-67. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23416893 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of DNA Double-Stranded Breaks Using the Comet Assay in Planarians.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2450:479-491. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2172-1_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35359324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juarez-Salinas H., Levi V., Jacobson E.L., Jacobson M.K. Poly(ADP-ribose) has a branched structure in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:607–609. - PubMed
-
- Tanuma S., Kanai Y. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of chromosomal proteins in the HeLa S3 cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:6565–6570. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Kim N.S., Haince J.F., Kang H.C., David K.K., Andrabi S.A., Poirier G.G., Dawson V.L., Dawson T.M. Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) binding to apoptosis-inducing factor is critical for PAR polymerase-1-dependent cell death (parthanatos) Sci. Signal. 2011;4:ra20. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

