Cationic Polymer Nanoparticles-Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Impairs Tumorigenicity of Prostate Cancer Cells
- PMID: 32013257
- PMCID: PMC7038067
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21030869
Cationic Polymer Nanoparticles-Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Impairs Tumorigenicity of Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
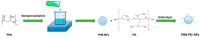
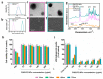
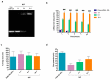
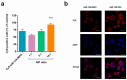
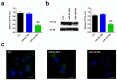
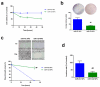
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role in regulating the expression of genes involved in tumor development, invasion, and metastasis. In particular, microRNA-124 (miR-124) modulates the expression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A) at the post-transcriptional level, impairing the ability of androgen-independent prostate cancer (PC3) cells to completely metabolize lipid substrates. However, the clinical translation of miRNAs requires the development of effective and safe delivery systems able to protect nucleic acids from degradation. Herein, biodegradable polyethyleneimine-functionalized polyhydroxybutyrate nanoparticles (PHB-PEI NPs) were prepared by aminolysis and used as cationic non-viral vectors to complex and deliver miR-124 in PC3 cells. Notably, the PHB-PEI NPs/miRNA complex effectively protected miR-124 from RNAse degradation, resulting in a 30% increase in delivery efficiency in PC3 cells compared to a commercial transfection agent (Lipofectamine RNAiMAX). Furthermore, the NPs-delivered miR-124 successfully impaired hallmarks of tumorigenicity, such as cell proliferation, motility, and colony formation, through CPT1A modulation. These results demonstrate that the use of PHB-PEI NPs represents a suitable and convenient strategy to develop novel nanomaterials with excellent biocompatibility and high transfection efficiency for cancer therapy.
Keywords: aminolysis; gene delivery; miR-124; polyethyleneimine (PEI); polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB); polymer nanoparticles; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-complexed antimiRs for inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis in prostate carcinoma and melanoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Nov 23;18(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00728-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 33228711 Free PMC article.
-
Photoluminescent and biodegradable polycitrate-polyethylene glycol-polyethyleneimine polymers as highly biocompatible and efficient vectors for bioimaging-guided siRNA and miRNA delivery.Acta Biomater. 2017 May;54:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.02.034. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28219808
-
Programing Assembling/Releasing Multifunctional miRNA Nanomedicine to Treat Prostate Cancer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Feb 26;12(8):9032-9040. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b21707. Epub 2020 Feb 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 31986004
-
Cationic microRNA-delivering nanocarriers for efficient treatment of colon carcinoma in xenograft model.Gene Ther. 2016 Dec;23(12):829-838. doi: 10.1038/gt.2016.60. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 27482839
-
Non-viral based miR delivery and recent developments.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Jul;128:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 29679644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting of Mcl-1 Expression by MiRNA-3614-5p Promotes Cell Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 11;23(8):4194. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084194. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457012 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines Targeting Metabolic Pathways in the Tumor Microenvironment: Future Perspectives and the Role of AI.Metabolites. 2025 Mar 13;15(3):201. doi: 10.3390/metabo15030201. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40137165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogenized Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in Pebax®Rnew. Thermal, Gas Transport and Antimicrobial Properties.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 25;12(6):1419. doi: 10.3390/polym12061419. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630521 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines in diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancers: an updated review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 21;12:1444201. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1444201. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39318666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA in prostate cancer: from biogenesis to applicative potential.BMC Urol. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01634-1. BMC Urol. 2024. PMID: 39506720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nuhn P., De Bono J.S., Fizazi K., Freedland S.J., Grilli M., Kantoff P.W., Sonpavde G., Sternberg C.N., Yegnasubramanian S., Antonarakis E.S. Update on Systemic Prostate Cancer Therapies: Management of Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer in the Era of Precision Oncology. Eur. Urol. 2019;75:88–99. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.03.028. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

