Pleiotropic Biological Effects of Dietary Phenolic Compounds and their Metabolites on Energy Metabolism, Inflammation and Aging
- PMID: 32013273
- PMCID: PMC7037231
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030596
Pleiotropic Biological Effects of Dietary Phenolic Compounds and their Metabolites on Energy Metabolism, Inflammation and Aging
Abstract
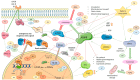
Dietary phenolic compounds are considered as bioactive compounds that have effects in different chronic disorders related to oxidative stress, inflammation process, or aging. These compounds, coming from a wide range of natural sources, have shown a pleiotropic behavior on key proteins that act as regulators. In this sense, this review aims to compile information on the effect exerted by the phenolic compounds and their metabolites on the main metabolic pathways involved in energy metabolism, inflammatory response, aging and their relationship with the biological properties reported in high prevalence chronic diseases. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated their pleiotropic molecular mechanisms of action and these findings raise the possibility that phenolic compounds have a wide variety of roles in different targets.
Keywords: aging; bioactive compounds; chronic disorders; inflammation; metabolites; oxidation; phenolic compounds; pleiotropic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Phenolic Compounds in Human Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects.Molecules. 2021 Dec 30;27(1):233. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010233. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Plant Phenolic Compounds and Their Importance in Human Nutrition and Management of Type 2 Diabetes.Molecules. 2016 Oct 15;21(10):1374. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101374. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27754463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential of Plant Phenolics in Prevention and Therapy of Skin Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 18;17(2):160. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020160. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26901191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Studies on Berry Bioactives and Their Health-Promoting Roles.Molecules. 2021 Dec 24;27(1):108. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010108. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenolic Compounds from Nuts: Extraction, Chemical Profiles, and Bioactivity.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Jan 29;68(4):927-942. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07160. Epub 2020 Jan 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 31910006 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Bioactive Effects of Five Plant Extracts with Different Phenolic Compositions against Different Therapeutic Targets.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;13(2):217. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020217. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397815 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Analytical Approaches for the Study of Bioavailability and Metabolism of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds.Molecules. 2022 Jan 25;27(3):777. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030777. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Dietary Fiber, Phenolic Compounds, and Fatty Acids on Mental Health: Possible Interactions with Genetic and Epigenetic Aspects.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 6;16(16):2578. doi: 10.3390/nu16162578. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-urolithiatic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Erica arborea flowers and leaves hydromethanolic extracts: An ethnopharmacological study.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Oct;30(10):103785. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103785. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37680977 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumae radix Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Mice with Chronic Neuroinflammation.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 26;11(8):2107. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082107. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wojdylo A., Oszmianski J., Czemerys R. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in 32 selected herbs. Food Chem. 2007;105:940–949. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.04.038. - DOI
-
- Barrajón-Catalán E., Fernández-Arroyo S., Saura D., Guillén E., Fernández-Gutiérrez A., Segura-Carretero A., Micol V. Cistaceae aqueous extracts containing ellagitannins show antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity, and cytotoxic activity against human cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010;48:2273–2282. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.05.060. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olaiya C.O., Soetan K.O., Esan A.M. The role of nutraceuticals, functional foods and value added food products in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. African J. Food Sci. 2016;10:185–193. doi: 10.5897/AJFS2015.1402. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

