Five-year Progression of Emphysema and Air Trapping at CT in Smokers with and Those without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Results from the COPDGene Study
- PMID: 32013794
- PMCID: PMC7104704
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020191429
Five-year Progression of Emphysema and Air Trapping at CT in Smokers with and Those without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Results from the COPDGene Study
Abstract
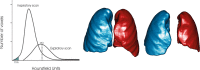
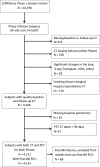
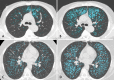
Background CT is used to quantify abnormal changes in the lung parenchyma of smokers that might overlap chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but studies on the progression of expiratory air trapping in smokers are scarce. Purpose To evaluate the relationship between longitudinal changes in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and CT-quantified emphysema and air trapping in smokers. Materials and Methods Cigarette smokers with and those without COPD participating in the multicenter observational COPDGene study were evaluated. Subjects underwent inspiratory and expiratory chest CT and spirometry at baseline and 5-year follow-up. Emphysema was quantified by using adjusted lung density (ALD). Air trapping was quantified by using mean lung density at expiratory CT and CT-measured functional residual capacity-to-total lung volume ratio. Linear models were used to regress quantitative CT measurements taken 5 years apart, and models were fit with and without adding FEV1 as a predictor. Analyses were stratified by Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) stage (GOLD 0, no COPD; GOLD 1, mild COPD; GOLD 2, moderate COPD; GOLD 3, severe COPD; GOLD 4, very severe COPD). Subjects with preserved FEV1-to-forced vital capacity ratio and reduced FEV1 percentage predicted were categorized as having preserved ratio impaired spirometry (PRISm). Results A total of 4211 subjects (503 with PRISm; 2034 with GOLD 0, 388 with GOLD 1, 816 with GOLD 2, 381 with GOLD 3, 89 with GOLD 4) were evaluated. ALD decreased by 1.7 g/L (95% confidence interval [CI]: -2.5, -0.9) in subjects with GOLD 0 at baseline and by 5.3 g/L (95% CI: -6.2, -4.4) in those with GOLD 1-4 (P < .001 for both). When adjusted for changes in FEV1, corresponding numbers were -2.2 (95% CI: -3.0, -1.3) and -4.6 g/L (95% CI: -5.6, -3.4) (P < .001 for both). Progression in air trapping was identified only in GOLD stage 2-4. Approximately 33%-50% of changes in air trapping in GOLD stages 2-4 were accounted for by changes in FEV1. Conclusion CT measures of emphysema and air trapping increased over 5 years in smokers. Forced expiratory volume in one second accounted for less than 10% of emphysema progression and less than 50% of air trapping progression detected at CT. © RSNA, 2020 Online supplemental material is available for this article.
Figures

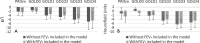

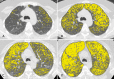
References
-
- Singh D, Agusti A, Anzueto A, et al. . Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: the GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur Respir J 2019;53(5):1900164. - PubMed
-
- Hogg JC. Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004;364(9435):709–721. - PubMed
-
- Bankier AA, De Maertelaer V, Keyzer C, Gevenois PA. Pulmonary emphysema: subjective visual grading versus objective quantification with macroscopic morphometry and thin-section CT densitometry. Radiology 1999;211(3):851–858. - PubMed
-
- Müller NL, Staples CA, Miller RR, Abboud RT. “Density mask”. An objective method to quantitate emphysema using computed tomography. Chest 1988;94(4):782–787. - PubMed
-
- Madani A, Van Muylem A, de Maertelaer V, Zanen J, Gevenois PA. Pulmonary emphysema: size distribution of emphysematous spaces on multidetector CT images--comparison with macroscopic and microscopic morphometry. Radiology 2008;248(3):1036–1041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

