6'-O-galloylpaeoniflorin regulates proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through AMPK/miR-299-5p/ATF2 axis
- PMID: 32014006
- PMCID: PMC6998290
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-020-1277-6
6'-O-galloylpaeoniflorin regulates proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through AMPK/miR-299-5p/ATF2 axis
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have shown 6'-O-galloylpaeoniflorin (GPF), a nature product extracted from the roots of paeoniflorin exerts anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effects of GPF on the proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells have not been clarified.
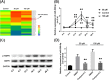
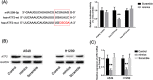
Methods: MTT assay was performed to determine the cytotoxicity of GPF treatment on NSCLC cells. Colony formation assay, cell scratch test and transwell assay were performed to determine the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells in vitro, respectively. An A549 cell xenograft mouse model was performed to confirm the growth of NSCLC cells in vivo. Western blotting was used to measure the levels of activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and phosph-AMPK (p-AMPK). Luciferase assay was used to validate the binding of miR-299-5p on the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of ATF2.
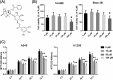
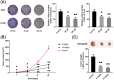
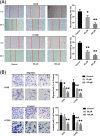
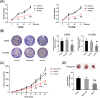
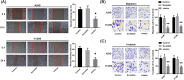
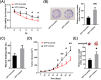
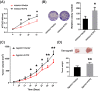
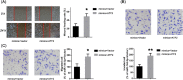
Results: Administration of GPF (50 or 100 μM) was significantly cytotoxic to A549 cells and H1299 cells, as well as inhibited the clonality, invasion and metastasis of NSCLC cells in vitro. GPF treatment also inhibited the tumor growth of NSCLC cell mouse xenografts in vivo. Exotic expression of miR-299-5p significantly inhibited the growth of NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo. Downregulation of miR-299-5p expression attenuated the inhibition of the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by GPF treatment. miR-299-5p significantly decreased ATF2 mRNA and protein levels in A549 cells (p < 0.05). Overexpression of ATF2 blocked the inhibitory effect of miR-299-5p on the proliferation and invasiveness of A549 cells.
Conclusions: GPF regulates miR-299-5p/ATF2 axis in A549 cells via the AMPK signalling pathway, thereby inhibiting the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Keywords: ATF2; metastasis; Non-small cell lung cancer; Proliferation; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Skřičková J, Kadlec B, Venclíček O, et al. Lung cancer. Cas Lek Cesk. 2018;157:226–236. - PubMed
-
- Brown T, Pilkington G, Bagust A, et al. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of first-line chemotherapy for adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17:1–278. doi: 10.3310/hta17060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

