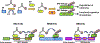The Skp2 Pathway: A Critical Target for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 32014608
- PMCID: PMC9201937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.01.013
The Skp2 Pathway: A Critical Target for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
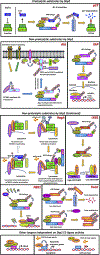
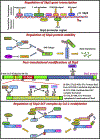
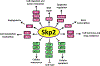
Strictly regulated protein degradation by ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is essential for various cellular processes whose dysregulation is linked to serious diseases including cancer. Skp2, a well characterized component of Skp2-SCF E3 ligase complex, is able to conjugate both K48-linked ubiquitin chains and K63-linked ubiquitin chains on its diverse substrates, inducing proteasome mediated proteolysis or modulating the function of tagged substrates respectively. Overexpression of Skp2 is observed in various human cancers associated with poor survival and adverse therapeutic outcomes, which in turn suggests that Skp2 engages in tumorigenic activity. To that end, the oncogenic properties of Skp2 are demonstrated by various genetic mouse models, highlighting the potential of Skp2 as a target for tackling cancer. In this article, we will describe the downstream substrates of Skp2 as well as upstream regulators for Skp2-SCF complex activity. We will further summarize the comprehensive oncogenic functions of Skp2 while describing diverse strategies and therapeutic platforms currently available for developing Skp2 inhibitors.
Keywords: Skp2-SCF complex; cancer targeting; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Wilkinson KD, Protein ubiquitination: a regulatory post-translational modification, Anti-cancer drug design 2 (2) (1987) 211–229. - PubMed
-
- Vucic D, Dixit VM, Wertz IE, Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: a post-translational modification at the edge of life and death, Nature reviews, Molecular cell biology 12 (7) (2011) 439–452. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama KI, Nakayama K, Ubiquitin ligases: cell-cycle control and cancer, Nature reviews, Cancer 6 (5) (2006) 369–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous