Drosophila YBX1 homolog YPS promotes ovarian germ line stem cell development by preferentially recognizing 5-methylcytosine RNAs
- PMID: 32015133
- PMCID: PMC7035628
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1910862117
Drosophila YBX1 homolog YPS promotes ovarian germ line stem cell development by preferentially recognizing 5-methylcytosine RNAs
Abstract
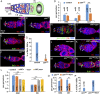
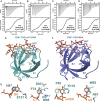
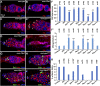
5-Methylcytosine (m5C) is a RNA modification that exists in tRNAs and rRNAs and was recently found in mRNAs. Although it has been suggested to regulate diverse biological functions, whether m5C RNA modification influences adult stem cell development remains undetermined. In this study, we show that Ypsilon schachtel (YPS), a homolog of human Y box binding protein 1 (YBX1), promotes germ line stem cell (GSC) maintenance, proliferation, and differentiation in the Drosophila ovary by preferentially binding to m5C-containing RNAs. YPS is genetically demonstrated to function intrinsically for GSC maintenance, proliferation, and progeny differentiation in the Drosophila ovary, and human YBX1 can functionally replace YPS to support normal GSC development. Highly conserved cold-shock domains (CSDs) of YPS and YBX1 preferentially bind to m5C RNA in vitro. Moreover, YPS also preferentially binds to m5C-containing RNAs, including mRNAs, in germ cells. The crystal structure of the YBX1 CSD-RNA complex reveals that both hydrophobic stacking and hydrogen bonds are critical for m5C binding. Overexpression of RNA-binding-defective YPS and YBX1 proteins disrupts GSC development. Taken together, our findings show that m5C RNA modification plays an important role in adult stem cell development.
Keywords: GSC; RNA methylation; YBX; YPS; m5C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dubin D. T., Stollar V., Methylation of Sindbis virus “26S” messenger RNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 66, 1373–1379 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Yang Y., et al. , RNA 5-methylcytosine facilitates the maternal-to-zygotic transition by preventing maternal mRNA decay. Mol. Cell. 75, 1188–1202.e11 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Chen X., et al. , 5-methylcytosine promotes pathogenesis of bladder cancer through stabilizing mRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 978–990 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

