Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer's dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5,000-person neuropathological study
- PMID: 32015339
- PMCID: PMC6997393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-14279-8
Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer's dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5,000-person neuropathological study
Abstract
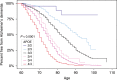
Each additional copy of the apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) allele is associated with a higher risk of Alzheimer's dementia, while the APOE2 allele is associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer's dementia, it is not yet known whether APOE2 homozygotes have a particularly low risk. We generated Alzheimer's dementia odds ratios and other findings in more than 5,000 clinically characterized and neuropathologically characterized Alzheimer's dementia cases and controls. APOE2/2 was associated with a low Alzheimer's dementia odds ratios compared to APOE2/3 and 3/3, and an exceptionally low odds ratio compared to APOE4/4, and the impact of APOE2 and APOE4 gene dose was significantly greater in the neuropathologically confirmed group than in more than 24,000 neuropathologically unconfirmed cases and controls. Finding and targeting the factors by which APOE and its variants influence Alzheimer's disease could have a major impact on the understanding, treatment and prevention of the disease.
Conflict of interest statement
E.B.L. receives royalties from UpToDate, and the other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG051504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061796/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030653/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066518/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L501542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002369/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015473/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N026004/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RF1 AG057902/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

