Effects of multiple injections on the efficacy and cytotoxicity of folate-targeted magnetite nanoparticles as theranostic agents for MRI detection and magnetic hyperthermia therapy of tumor cells
- PMID: 32015364
- PMCID: PMC6997166
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-58605-3
Effects of multiple injections on the efficacy and cytotoxicity of folate-targeted magnetite nanoparticles as theranostic agents for MRI detection and magnetic hyperthermia therapy of tumor cells
Abstract
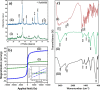
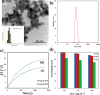
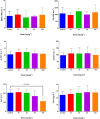
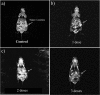
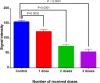
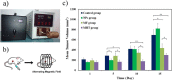
Folate-targeted iron oxide nanoparticles (FA@Fe3O4 NPs) were prepared by a one-pot hydrothermal method and then used as cancer theranostic agents by combining magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic hyperthermia therapy (MHT). Crystal structure, morphology, magnetic properties, surface functional group, and heating efficacy of the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by XRD, TEM, VSM, FTIR, and hyperthermia analyses. The results indicated that the crystal structure, magnetic properties, and heating efficacy of the magnetite nanoparticles were improved by hydrothermal treatment. Toxicity of the prepared NPs was assessed in vitro and in vivo on the mammary cells and BALB/c mice, respectively. The results of the in vitro toxicity analysis showed that the FA@Fe3O4 NPs are relatively safe even at high concentrations of the NPs up to 1000 µg mL-1. Also, the targetability of the FA@Fe3O4 NPs for the detection of folate over-expressed cancer cells was evaluated in an animal model of breast tumor using MRI analysis. It was observed that T2-weighted magnetic resonance signal intensity was decreased with the three-time injection of the FA@Fe3O4 NPs with 24 h interval at a safe dose (50 mg kg-1), indicating the accumulation and retention of the NPs within the tumor tissues. Moreover, the therapeutic efficacy of the MHT using the FA@Fe3O4 NPs was evaluated in vivo in breast tumor-bearing mice. Hyperthermia treatment was carried out under a safe alternating magnetic field permissible for magnetic hyperthermia treatment (f = 150 kHz, H = 12.5 mT). The therapeutic effects of the MHT were evaluated by monitoring the tumor volume during the treatment period. The results showed that the mice in the control group experienced an almost 3.5-fold increase in the tumor volume during 15 days, while, the mice in the MHT group had a mild increase in the tumor volume (1.8-fold) within the same period (P < 0.05). These outcomes give promise that FA@Fe3O4 NPs can be used as theranostic agents for the MRI and MHT applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Soleymani M, Edrissi M, Alizadeh AM. Thermosensitive polymer-coated La 0.73 Sr 0.27 MnO 3 nanoparticles: potential applications in cancer hyperthermia therapy and magnetically activated drug delivery systems. Polymer Journal. 2015;47:797. doi: 10.1038/pj.2015.66. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

