Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced metabolic stress by limiting oxidative damage to the mitochondria from brown adipose tissue
- PMID: 32015410
- PMCID: PMC7062825
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-020-0379-z
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced metabolic stress by limiting oxidative damage to the mitochondria from brown adipose tissue
Erratum in
-
Correction: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 protects mice from high-fat diet-induced metabolic stress by limiting oxidative damage to the mitochondria from brown adipose tissue.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jun;52(6):988. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0451-8. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32541817 Free PMC article.
Abstract
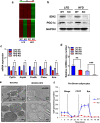
Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) is an NADP+-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate in the mitochondrial matrix, and is critical for the production of NADPH to limit the accumulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Here, we showed that high-fat diet (HFD) feeding resulted in accelerated weight gain in the IDH2KO mice due to a reduction in whole-body energy expenditure. Moreover, the levels of NADP+, NADPH, NAD+, and NADH were significantly decreased in the brown adipose tissue (BAT) of the HFD-fed IDH2KO animals, accompanied by decreased mitochondrial function and reduced expression of key genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis, energy expenditure, and ROS resolution. Interestingly, these changes were partially reversed when the antioxidant butylated hydroxyanisole was added to the HFD. These observations reveal a crucial role for IDH2 in limiting ROS-dependent mitochondrial damage when BAT metabolism is normally enhanced to limit weight gain in response to dietary caloric overload.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017R1A2B3006406/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)/International
- R01 HL048044/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HR18C0012/Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI)/International
- 2015R1D1A1AO1057610/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)/International
- 27307C0012/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

