Distribution and storage of inflammatory memory in barrier tissues
- PMID: 32015472
- PMCID: PMC7547402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0263-z
Distribution and storage of inflammatory memory in barrier tissues
Abstract
Memories of previous immune events enable barrier tissues to rapidly recall distinct environmental exposures. To effectively inform future responses, these past experiences can be stored in cell types that are long-term residents or essential constituents of tissues. There is an emerging understanding that, in addition to antigen-specific immune cells, diverse haematopoietic, stromal, parenchymal and neuronal cell types can store inflammatory memory. Here, we explore the impact of previous immune activity on various cell lineages with the goal of presenting a unified view of inflammatory memory to environmental exposures (such as allergens, antigens, noxious agents and microorganisms) at barrier tissues. We propose that inflammatory memory is distributed across diverse cell types and stored through shifts in cell states, and we provide a framework to guide future experiments. This distribution and storage may promote adaptation or maladaptation in homeostatic, maintenance and disease settings - especially if the distribution of memory favours cellular cooperation during storage or recall.
Figures

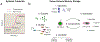

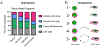
References
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S & Medzhitov R Recognition of commensal microflora by Toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 118, 229–241 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Arendt D et al. The origin and evolution of cell types. Nat Rev Genet 17, 744–757 (2016). - PubMed
-
-
Okabe Y & Medzhitov R Tissue biology perspective on macrophages. Nat. Immunol 17, 9–17 (2015).
This Review discusses the role of macrophages in tissue biology with a focus on cell type diversification and specialization from an evolutionary and transcriptional perspective.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL095791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI138546/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DP2 GM119419/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI039671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U2C CA233195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI118672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG006193/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA217377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA046277/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

