Rethinking mucosal antibody responses: IgM, IgG and IgD join IgA
- PMID: 32015473
- PMCID: PMC10262260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0261-1
Rethinking mucosal antibody responses: IgM, IgG and IgD join IgA
Abstract
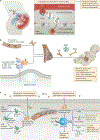
Humoral immune responses at mucosal surfaces have historically focused on IgA. Growing evidence highlights the complexity of IgA-inducing pathways and the functional impact of IgA on mucosal commensal bacteria. In the gut, IgA contributes to the establishment of a mutualistic host-microbiota relationship that is required to maintain homeostasis and prevent disease. This Review discusses how mucosal IgA responses occur in an increasingly complex humoral defence network that also encompasses IgM, IgG and IgD. Aside from integrating the protective functions of IgA, these hitherto neglected mucosal antibodies may strengthen the communication between mucosal and systemic immune compartments.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sansonetti PJ War and peace at mucosal surfaces. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 953–964 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Kato LM, Kawamoto S, Maruya M & Fagarasan S The role of the adaptive immune system in regulation of gut microbiota. Immunol. Rev 260, 67–75 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Macpherson AJ, Yilmaz B, Limenitakis JP & Ganal-Vonarburg SC IgA function in relation to the intestinal microbiota. Annu. Rev. Immunol 36, 359–381 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Peterson DA, McNulty NP, Guruge JL & Gordon JI IgA response to symbiotic bacteria as a mediator of gut homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2, 328–339 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

