N6-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I
- PMID: 32015498
- PMCID: PMC7137398
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-019-0653-9
N6-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I
Abstract
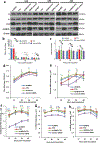
Internal N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is one of the most common and abundant modifications of RNA. However, the biological roles of viral RNA m6A remain elusive. Here, using human metapneumovirus (HMPV) as a model, we demonstrate that m6A serves as a molecular marker for innate immune discrimination of self from non-self RNAs. We show that HMPV RNAs are m6A methylated and that viral m6A methylation promotes HMPV replication and gene expression. Inactivating m6A addition sites with synonymous mutations or demethylase resulted in m6A-deficient recombinant HMPVs and virion RNAs that induced increased expression of type I interferon, which was dependent on the cytoplasmic RNA sensor RIG-I, and not on melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5). Mechanistically, m6A-deficient virion RNA induces higher expression of RIG-I, binds more efficiently to RIG-I and facilitates the conformational change of RIG-I, leading to enhanced interferon expression. Furthermore, m6A-deficient recombinant HMPVs triggered increased interferon in vivo and were attenuated in cotton rats but retained high immunogenicity. Collectively, our results highlight that (1) viruses acquire m6A in their RNA as a means of mimicking cellular RNA to avoid detection by innate immunity and (2) viral RNA m6A can serve as a target to attenuate HMPV for vaccine purposes.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
C.H. is a scientific founder of Accent Therapeutics, Ins. J.L., C.H., M.E.P., and S.N. are filing a provision patent application of 62/748,175.
Figures


Comment in
-
Viral RNA in an m6A disguise.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Apr;5(4):531-532. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0689-x. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32218507 No abstract available.
References
-
- Loo YM & Gale M Jr. Viral regulation and evasion of the host response. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol 316, 295–313 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Chow KT, Gale M Jr. & Loo YM RIG-I and Other RNA Sensors in Antiviral Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol 36, 667–694 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Hornung V et al. 5’-Triphosphate RNA is the ligand for RIG-I. Science 314, 994–997 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

