Changes in the expression of Notch and Wnt signalling molecules in human endometrial cancer
- PMID: 32015673
- PMCID: PMC6992362
- DOI: 10.6001/actamedica.v26i3.4148
Changes in the expression of Notch and Wnt signalling molecules in human endometrial cancer
Abstract
Background: Endometrial cancer is the sixth most frequent type of cancer among women worldwide. Type I adenocarcinomas account for 80-85% of endometrial cancer cases and sometimes require more aggressive treatment than the remaining part of this group. Therefore, molecular markers to stratify adenocarcinomas are needed.
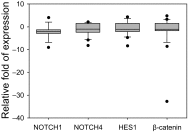
Materials and methods: In this study, we analysed Notch and Wnt signalling in human endometrial cancer cases to evaluate these pathway elements as potential biomarkers for type I endometrial cancer. Endometrial samples were obtained from 47 women undergoing surgery for stage I-IV endometrial cancer in the National Cancer Institute (Vilnius, Lithuania) in 2015-2016. The expression at the mRNA level of signalling molecules genes (NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, NOTCH4, JAG1, JAG2, DLL1, HES1, AXIN2 and CTNNB1) was analysed by the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Relative expression of NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HES1 and β-catenin proteins in endometrioid adenocarcinoma was evaluated by the Western blot method.
Results: The expression level of Notch receptors, ligands, and the target gene, as well as CTNNB1 and AXIN2, was reduced in stage I endometrioid adenocarcinoma if compared to the adjacent non-tumour tissue. The expression of all receptors, ligands, and target molecules was reduced in adenocarcinomas of later stages. The statistically significant correlations between transcript amounts of Notch receptors and ligands were found. There was a statistically significant difference in the gene expression of Notch signalling pathway components between different tumour differentiation grade samples. A positive correlation between mRNA and protein the expression level of NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HES1 was determined in stage I samples.
Conclusions: Analysis of 47 human endometrial cancer samples revealeda reduction in the transcript levels of Notch and Wnt signalling molecule compared to the adjacent non-tumour tissue. These results suggest tumour suppressor function of Notch and Wnt signalling in human endometrial cancer. More detailed research on these signalling pathways should reveal their importance as potential biomarkers.
SantraukaĮvadas. Endometriumo vėžys yra šeštas pagal dažnį moterų piktybinis navikas pasaulyje. I tipo adenokarcinomos sudaro 80–85 % endometriumo vėžio atvejų. Siekiant parinkti adekvatų endometriumo adenokarcinomos gydymą gali padėti molekuliniai žymenys.Medžiaga ir metodika. Atliekant šį tyrimą išanalizuoti Notch ir Wnt signalinių kelių komponentų ypatumai žmogaus endometriumo vėžio atveju siekiant įvertinti šių kelių komponentų, kaip potencialių I tipo endometriumo vėžio biožymenų, galimybes. Gimdos kūno audinio mėginiai gauti iš 2015–2016 m. Nacionaliniame vėžio institute (Vilnius, Lietuva) operuotų I–IV stadijos gimdos kūno vėžiu sergančių pacienčių (n = 47) operacinės medžiagos. Notch (NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, NOTCH4, JAG1, JAG2, DLL1, HES1) ir Wnt (AXIN2, CTNNB1) signalinių kelių genų raiška analizuota naudojant kiekybinį polimerazės grandininės reakcijos metodą. Santykinis NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HES1 ir β-katenino baltymų kiekis endometrioidinės adenokarcinomos mėginiuose buvo įvertintas Western blot metodu.Rezultatai. Notch receptorių, ligandų ir taikinio, taip pat CTNNB1 ir AXIN2 genų raiška buvo sumažėjusi I stadijos endometrioidinės adenokarcinomos audiniuose, palyginti su aplinkiniu sveiku audiniu. Tirtų receptorių, ligandų ir taikinio genų raiška buvo sumažėjusi vėlesnių stadijų adenokarcinomų audiniuose. Nustatyta statistiškai reikšminga koreliacija tarp Notch receptorių ir ligandų transkriptų kiekio. Taip pat nustatyti statistiškai reikšmingi Notch signalinio kelio komponentų genų raiškos skirtumai esant skirtingai naviko diferenciacijai. Nustatyta teigiama koreliacija tarp NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HES1 genų raiškos ir baltymų kiekio ligos I stadijos atveju.Išvados. Išanalizavus 47-ių pacienčių endometriumo vėžio mėginius nustatytas Notch ir Wnt signalinių molekulių raiškos sumažėjimas, palyginti su jų raiška aplinkiniame sveikajame audinyje. Tyrimo rezultatai leidžia teigti, kad Notch ir Wnt signalai turi naviką slopinantį potencialą endometriumo vėžio atveju. Išsamesni atskirų šių signalinių kelių komponentų tyrimai turėtų atskleisti jų, kaip potencialių biožymenų, svarbą.Raktažodžiai: Notch, WNT signalinis kelias, endometriumo vėžys.
Keywords: Notch; WNT signalling pathway; endometrial cancer.
© Lietuvos mokslų akademija, 2019.
Figures


References
-
- Ferlay J Soerjomataram I Dikshit R Eser S Mathers C Rebelo M et al. . Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136: E359–E86. - PubMed
-
- Kitchener HC, Trimble EL. Endometrial Cancer Working Group of the Gynecologic Cancer Intergroup: Endometrial cancer state of the science meeting. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009; 19: 134–40. - PubMed
-
- Hubbard SA, Friel AM, Kumar B, Zhang L, Rueda BR, Gargett CE. Evidence for cancer stem cells in human endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 8241–8. - PubMed
-
- Kalampokas E, Payne F, Gurumurthy M. An update on the use of immunohistochemistry and molecular pathology in the diagnosis of pre-invasive and malignant lesions in gynecological oncology. Gynecol Oncol. 2018; 150: 378–86. - PubMed
-
- Dunford RG, Mejia EB, Salbador GW, Gerth WA, Hampson NB. Diving methods and decompression sickness incidence of Miskito Indian underwater harvesters. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2002; 29: 74–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
