Molecular diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, and antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 32015881
- PMCID: PMC6988205
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-020-0429-6
Molecular diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, and antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
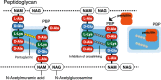
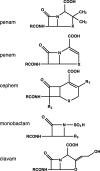
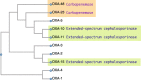
Along with the recent spread of multidrug-resistant bacteria, outbreaks of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) and carbapenemase-producing bacteria present a serious challenge to clinicians. β-lactam antibiotics are the most frequently used antibacterial agents and ESBLs, and carbapenemases confer resistance not only to carbapenem antibiotics but also to penicillin and cephem antibiotics. The mechanism of β-lactam resistance involves an efflux pump, reduced permeability, altered transpeptidases, and inactivation by β-lactamases. Horizontal gene transfer is the most common mechanism associated with the spread of extended-spectrum β-lactam- and carbapenem resistance among pathogenic bacterial species. Along with the increase in antimicrobial resistance, many different types of ESBLs and carbapenemases have emerged with different enzymatic characteristics. For example, carbapenemases are represented across classes A to D of the Ambler classification system. Because bacteria harboring different types of ESBLs and carbapenemases require specific therapeutic strategies, it is essential for clinicians to understand the characteristics of infecting pathogens. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on carbapenem resistance by ESBLs and carbapenemases, such as class A carbapenemases, class C extended-spectrum AmpC (ESAC), carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamases (CHDLs), and class B metallo-β-lactamases, with the aim of aiding critical care clinicians in their therapeutic decision making.
Keywords: Carbapenemase; Classification; Multidrug resistance; β-Lactam; β-Lactamase.
© The Author(s). 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsTS has a patent for immunization with PcrV from the Regent of the University of California (Berkeley, CA, USA). All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



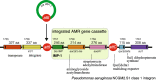
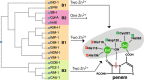

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

