The outcome of Y-V plasty as a final option in patients with recurrent bladder neck sclerosis following failed endoscopic treatment
- PMID: 32015912
- PMCID: PMC6979556
- DOI: 10.5173/ceju.2019.1977
The outcome of Y-V plasty as a final option in patients with recurrent bladder neck sclerosis following failed endoscopic treatment
Abstract
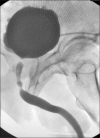
Introduction: Bladder neck sclerosis is a rare late complication of transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Endoscopic resection or incision of the bladder neck is usually successful in the management of such cases. In some cases, even repeated endoscopic management always followed with recurrent sclerosis. In these cases, the Y-V plasty of the bladder neck provides a final option of treatment.
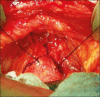
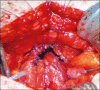
Material and methods: Retrospective evaluation of 24 patients who underwent Y-V plasty of the bladder neck from 2007 to 2014 was performed. All patients had TURP once and presented after at least 2 failed attempts of endoscopic management. The principle of this technique is to insert a V-shaped part of the bladder wall into the fibrosed bladder neck. The patient evaluation included measuring Q max, residual urine volume and asking about their satisfaction. All patients were operated in the same center by the same surgeon.
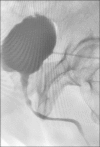
Results: The mean age of patients at surgery was 66.8 years (range 56-74 years). All patients presented preoperatively with obstructive micturition with mean Qmax 2.2 ml/s (SD ±1.9) and mean residual urine volume of 381 ±169 ml. After a mean follow-up of 46 months (SD ±22), the mean Qmax reached 16.4 ml/s (SD 3.3) while the mean residual urine volume was 18 ml (SD ±6). Recurrent sclerosis occurred in three patients (12.5%). A total of 94.1% of patients reported satisfactory micturition with significant improvement in the quality of life.
Conclusions: The Y-V plasty can provide a final option with a high success rate for patients with bladder neck sclerosis after failed endoscopic treatment.
Keywords: benign; bladder neck contracture; bladder reconstruction; hyperplasia; prostatic hypertrophy; stricture recurrence.
Copyright by Polish Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistent storage symptoms following Y-V plasty reconstruction for the treatment of refractory bladder neck contracture.Neurourol Urodyn. 2022 Jun;41(5):1082-1090. doi: 10.1002/nau.24941. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Neurourol Urodyn. 2022. PMID: 35481590
-
The T-plasty: a modified YV-plasty for highly recurrent bladder neck contracture after transurethral surgery for benign hyperplasia of the prostate: clinical outcome and patient satisfaction.World J Urol. 2016 Oct;34(10):1437-42. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1779-5. Epub 2016 Feb 12. World J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26873595
-
Effectiveness of Y-V-plasty for refractory bladder neck stenosis after transurethral prostate surgery.Int J Urol. 2025 Apr;32(4):434-440. doi: 10.1111/iju.15676. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Int J Urol. 2025. PMID: 39801036
-
[Bladder neck sclerosis following prostate surgery : Which therapy when?].Urologe A. 2017 Sep;56(9):1129-1138. doi: 10.1007/s00120-017-0431-3. Urologe A. 2017. PMID: 28646238 Review. German.
-
Monopolar transurethral resection of the big prostate, experience at Prince Hussein Bin Abdullah Urology Center.J Pak Med Assoc. 2011 Jul;61(7):628-31. J Pak Med Assoc. 2011. PMID: 22204233 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of urethral strictures and stenosis caused by the endo-urological treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia-a single-center experience.Asian J Urol. 2023 Apr;10(2):137-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2021.06.009. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Asian J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36942121 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic Bladder Neck Wedge Resection with Preservation of the Posterior Urethral Bed Versus Transurethral Resection of the Bladder Neck for Refractory Bladder Neck Contracture: A Comparative Study.Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025 Aug 11;79:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2025.07.014. eCollection 2025 Sep. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2025. PMID: 40832460 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary Outcomes after Transurethral Procedures for Bladder Neck Contracture Following Endoscopic Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 29;10(13):2884. doi: 10.3390/jcm10132884. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34209631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mayer EK, Kroeze SG, Chopra S, Bottle A, Patel A. Examining the 'gold standard': a comparative critical analysis of three consecutive decades of monopolar transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) outcomes. BJU Int. 2012;110:1595–601. - PubMed
-
- Sikafi Z, Butler MR, Lane V, O'Flynn JD, Fitzpatrick JM. Bladder neck contracture following prostatectomy. Br J Urol. 1985;57:308–310. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Pan JH, Liu QG, et al. Selective trans-urethral resection of the prostate combined with transurethral incision of the bladder neck for bladder outlet obstruction in patients with small-volume benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH): a prospective randomized study. PLoS ONE. 2013;9:e63227. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cindolo L, Marchioni M, Emiliani E, et al. Bladder neck contracture after surgery for benign prostatic obstruction. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017;69:133–143. - PubMed
-
- Pansadoro V, Emiliozzi P. Iatrogenic prostatic urethralstrictures: classification and endoscopic treatment. Urology. 1999;53:784–789. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
