REXTAL: Regional Extension of Assemblies Using Linked-Reads
- PMID: 32016171
- PMCID: PMC6996091
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-94968-0_6
REXTAL: Regional Extension of Assemblies Using Linked-Reads
Abstract
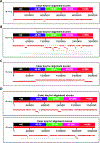
It is currently impossible to get complete de-novo assembly of segmentally duplicated genome regions using genome-wide short-read datasets. Here, we devise a new computational method called Regional Extension of Assemblies Using Linked-Reads (REXTAL) for improved region-specific assembly of segmental duplication-containing DNA, leveraging genomic short-read datasets generated from large DNA molecules partitioned and barcoded using the "Gel Bead in Emulsion" (GEM) microfluidic method (Zheng et al., 2016). We show that using REXTAL, it is possible to extend assembly of single-copy diploid DNA into adjacent, otherwise inaccessible subtelomere segmental duplication regions and other subtelomeric gap regions. Moreover, REXTAL is computationally more efficient for the directed assembly of such regions from multiple genomes (e.g., for the comparison of structural variation) than genome-wide assembly approaches.
Keywords: 10X sequencing; Linked-read sequencing; Subtelomere; assembly; genome gaps; segmental duplication; structural variation.
Figures

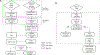
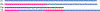
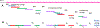


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
