Evaluation of penicillin G susceptibility testing methods for Staphylococcus lugdunensis
- PMID: 32016343
- PMCID: PMC7177478
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkaa004
Evaluation of penicillin G susceptibility testing methods for Staphylococcus lugdunensis
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus lugdunensis belongs to the CoNS group, but is regarded to be more virulent than most other CoNS. It is also remarkably susceptible to antibiotics, including penicillin G.
Objectives: To evaluate different methods for penicillin susceptibility testing, to assess penicillin susceptibility rates among S. lugdunensis and to describe the clinical presentation including antibiotic treatment.
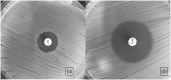
Methods: Clinical isolates of S. lugdunensis were tested for penicillin susceptibility using disc diffusion according to CLSI (10 U disc) and EUCAST (1 U disc), assessment of zone-edge appearance, nitrocefin test and Etest for MIC determination. PCR of the blaZ gene was used as a reference method.
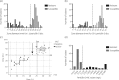
Results: Of the 112 isolates included in the study, 67% were susceptible to penicillin G according to blaZ PCR. The EUCAST disc diffusion test had 100% sensitivity, whereas the CLSI method had one very major error with a false-susceptible isolate. When zone-edge appearance was included in the assessment, the false-susceptible isolate was correctly classified as resistant. Foreign-body infection was the most common focus of infection, affecting 49% of the participants. Only 4% of the patients were treated with penicillin G.
Conclusions: Penicillin susceptibility is common in S. lugdunensis and the disc diffusion method according to EUCAST had a higher sensitivity than that of CLSI. Assessment of zone-edge appearance could increase the sensitivity of the disc diffusion test. Penicillin susceptibility testing and treatment should be considered in S. lugdunensis infections.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Ravaioli S, Selan L, Visai L. et al. Staphylococcus lugdunensis, an aggressive coagulase-negative pathogen not to be underestimated. Int J Artif Organs 2012; 35: 742–53. - PubMed
-
- Seng P, Traore M, Lavigne JP. et al. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: a neglected pathogen of infections involving fracture-fixation devices. Int Orthop 2017; 41: 1085–91. - PubMed
-
- Lourtet-Hascoet J, Bicart-See A, Felice MP. et al. Staphylococcus lugdunensis, a serious pathogen in periprosthetic joint infections: comparison to Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Int J Infect Dis 2016; 51: 56–61. - PubMed
-
- Argemi X, Prevost G, Riegel P. et al. VISLISI trial, a prospective clinical study allowing identification of a new metalloprotease and putative virulence factor from Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2017; 23: 334.e1–8. - PubMed

