Macroalgal-bacterial interactions: identification and role of thallusin in morphogenesis of the seaweed Ulva (Chlorophyta)
- PMID: 32016363
- PMCID: PMC7289720
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/eraa066
Macroalgal-bacterial interactions: identification and role of thallusin in morphogenesis of the seaweed Ulva (Chlorophyta)
Abstract
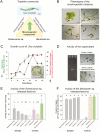
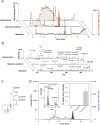
Macroalgal microbiomes have core functions related to biofilm formation, growth, and morphogenesis of seaweeds. In particular, the growth and development of the sea lettuce Ulva spp. (Chlorophyta) depend on bacteria releasing morphogenetic compounds. Under axenic conditions, the macroalga Ulva mutabilis develops a callus-like phenotype with cell wall protrusions. However, co-culturing with Roseovarius sp. (MS2) and Maribacter sp. (MS6), which produce various stimulatory chemical mediators, completely recovers morphogenesis. This ecological reconstruction forms a tripartite community which can be further studied for its role in cross-kingdom interactions. Hence, our study sought to identify algal growth- and morphogenesis-promoting factors (AGMPFs) capable of phenocopying the activity of Maribacter spp. We performed bioassay-guided solid-phase extraction in water samples collected from U. mutabilis aquaculture systems. We uncovered novel ecophysiological functions of thallusin, a sesquiterpenoid morphogen, identified for the first time in algal aquaculture. Thallusin, released by Maribacter sp., induced rhizoid and cell wall formation at a concentration of 11 pmol l-1. We demonstrated that gametes acquired the iron complex of thallusin, thereby linking morphogenetic processes with intracellular iron homeostasis. Understanding macroalgae-bacteria interactions permits further elucidation of the evolution of multicellularity and cellular differentiation, and development of new applications in microbiome-mediated aquaculture systems.
Keywords: Algal growth; cell wall; cross-kingdom interaction; morphogenesis; morphogenesis-promoting factor; phytohormone; rhizoid; seaweed; siderophore.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures


References
-
- Amin SA, Hmelo LR, van Tol HM, et al. 2015. Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria. Nature 522, 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Blomster J, Bäck S, Fewer DP, Kiirikki M, Lehvo A, Maggs CA, Stanhope MJ. 2002. Novel morphology in Enteromorpha (Ulvophyceae) forming green tides. American Journal of Botany 89, 1756–1763. - PubMed
-
- Butler A. 1998. Acquisition and utilization of transition metal ions by marine organisms. Science 281, 207–210. - PubMed
-
- Califano G, Wichard T. 2018. Preparation of axenic cultures in Ulva (Chlorophyta). In: Charrier B, Wichard T, Reddy C, eds. Protocols for macroalgae research. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 159–173.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

