Differential evolution in 3'UTRs leads to specific gene expression in Staphylococcus
- PMID: 32016395
- PMCID: PMC7049690
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa047
Differential evolution in 3'UTRs leads to specific gene expression in Staphylococcus
Abstract
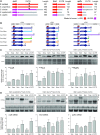
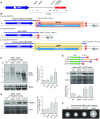
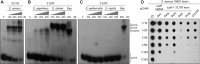
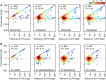
The evolution of gene expression regulation has contributed to species differentiation. The 3' untranslated regions (3'UTRs) of mRNAs include regulatory elements that modulate gene expression; however, our knowledge of their implications in the divergence of bacterial species is currently limited. In this study, we performed genome-wide comparative analyses of mRNAs encoding orthologous proteins from the genus Staphylococcus and found that mRNA conservation was lost mostly downstream of the coding sequence (CDS), indicating the presence of high sequence diversity in the 3'UTRs of orthologous genes. Transcriptomic mapping of different staphylococcal species confirmed that 3'UTRs were also variable in length. We constructed chimeric mRNAs carrying the 3'UTR of orthologous genes and demonstrated that 3'UTR sequence variations affect protein production. This suggested that species-specific functional 3'UTRs might be specifically selected during evolution. 3'UTR variations may occur through different processes, including gene rearrangements, local nucleotide changes, and the transposition of insertion sequences. By extending the conservation analyses to specific 3'UTRs, as well as the entire set of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis mRNAs, we showed that 3'UTR variability is widespread in bacteria. In summary, our work unveils an evolutionary bias within 3'UTRs that results in species-specific non-coding sequences that may contribute to bacterial diversity.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Gripenland J., Netterling S., Loh E., Tiensuu T., Toledo-Arana A., Johansson J.. RNAs: regulators of bacterial virulence. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2010; 8:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Bouloc P., Repoila F.. Fresh layers of RNA-mediated regulation in Gram-positive bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016; 30:30–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

