Development of an Ewing sarcoma cell line with resistance to EWS‑FLI1 inhibitor YK‑4‑279
- PMID: 32016454
- PMCID: PMC8371434
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10948
Development of an Ewing sarcoma cell line with resistance to EWS‑FLI1 inhibitor YK‑4‑279
Abstract
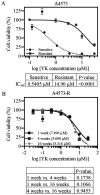
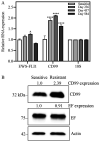
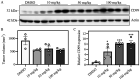
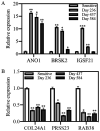
Despite Ewing sarcoma (ES) being the second most common pediatric malignancy of bone and soft tissue, few novel therapeutic approaches have been introduced over the past few decades. ES contains a pathognomonic chromosomal translocation that leads to a fusion protein between EWSR1 and an ets family member, most often FLI1. EWS‑FLI1 is the most common type of fusion protein and is a well‑vetted therapeutic target. A small molecule inhibitor of EWS‑FLI1, YK‑4‑279 (YK) was developed with the intention to serve as a targeted therapy option for patients with ES. The present study investigated resistance mechanisms by developing an ES cell line specifically resistant to YK. The ES cell line A4573 was treated with YK to create resistant cells by long term continuous exposure. The results revealed that resistance in A4573 was robust and sustainable, with a >27‑fold increase in IC50 lasting up to 16 weeks in the absence of the compound. Resistant ES cells were still sensitive to standard of care drugs, including doxorubicin, vincristine and etoposide, which may be valuable in future combination treatments in the clinic. Resistant ES cells revealed an increased expression of CD99. RNA sequencing and qPCR validation of resistant ES cells confirmed an increased expression of ANO1, BRSK2 and IGSF21, and a reduced expression of COL24A1, PRSS23 and RAB38 genes. A functional association between these genes and mechanism of resistance remains to be investigated. The present study created a cell line to investigate YK resistance.
Keywords: ewing sarcoma; YK-4-279; resistance; eWS-Fli1; cd99; ano1.
Figures

References
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Melot T, Garau XS, Zucker JM, Lenoir GM, Ambros PF, Sheer D, Turc-Carel C, Triche TJ, et al. The Ewing family of tumors-a subgroup of small-round-cell tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:294–299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199408043310503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- May WA, Gishizky ML, Lessnick SL, Lunsford LB, Lewis BC, Delattre O, Zucman J, Thomas G, Denny CT. Ewing sarcoma 11;22 translocation produces a chimeric transcription factor that requires the DNA-binding domain encoded by FLI1 for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:5752–5756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5752. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

