Non-intrinsic ATP-binding cassette proteins ABCI19, ABCI20 and ABCI21 modulate cytokinin response at the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 32016506
- PMCID: PMC7346704
- DOI: 10.1007/s00299-019-02503-0
Non-intrinsic ATP-binding cassette proteins ABCI19, ABCI20 and ABCI21 modulate cytokinin response at the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
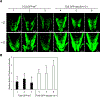
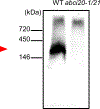
The non-intrinsic ABC proteins ABCI20 and ABCI21 are induced by light under HY5 regulation, localize to the ER, and ameliorate cytokinin-driven growth inhibition in young Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. The plant ATP-binding cassette (ABC) I subfamily (ABCIs) comprises heterogeneous proteins containing any of the domains found in other ABC proteins. Some ABCIs are known to function in basic metabolism and stress responses, but many remain functionally uncharacterized. ABCI19, ABCI20, and ABCI21 of Arabidopsis thaliana cluster together in a phylogenetic tree, and are suggested to be targets of the transcription factor ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 (HY5). Here, we reveal that these three ABCIs are involved in modulating cytokinin responses during early seedling development. The ABCI19, ABCI20 and ABCI21 promoters harbor HY5-binding motifs, and ABCI20 and ABCI21 expression was induced by light in a HY5-dependent manner. abci19 abci20 abci21 triple and abci20 abci21 double knockout mutants were hypersensitive to cytokinin in seedling growth retardation assays, but did not show phenotypic differences from the wild type in either control medium or auxin-, ABA-, GA-, ACC- or BR-containing media. ABCI19, ABCI20, and ABCI21 were expressed in young seedlings and the three proteins interacted with each other, forming a large protein complex at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. These results suggest that ABCI19, ABCI20, and ABCI21 fine-tune the cytokinin response at the ER under the control of HY5 at the young seedling stage.
Keywords: ABC transporter; Cytokinin; Endoplasmic reticulum; HY5; Seedling growth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Ali T, Bednarska J, Vassilopoulos S, Tran M, Diakonov IA, Ziyadeh-Isleem A, Guicheney P, Gorelik J, Korchev YE, Reilly MM, Bitoun M, Shevchuk A (2019) Correlative SICM-FCM reveals changes in morphology and kinetics of endocytic pits induced by disease-associated mutations in dynamin. Faseb j 33:8504–8518 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ang LH, Chattopadhyay S, Wei N, Oyama T, Okada K, Batschauer A, Deng XW (1998) Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol Cell 1:213–222 - PubMed
-
- Chang CS, Li YH, Chen LT, Chen WC, Hsieh WP, Shin J, Wu SH (2008) LZF1, a HY5-regulated transcriptional factor, functions in Arabidopsis de-etiolation. Plant J 54:205–219 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

